Drug Catalog - Product Detail
AMIDATE IV SOL 2MG/ML 10ML X 10
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00409-6695-01 | HOSPIRA | 10 | 2MG/ML | SOLUTION |
PACKAGE FILES





Generic Name
ETOMIDATE
Substance Name
ETOMIDATE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
INTRAVENOUS
Application Number
NDA018227
Description
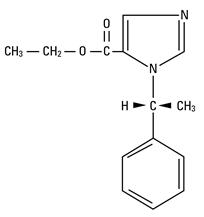
DESCRIPTION AMIDATE (Etomidate Injection, USP) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution. Each milliliter contains etomidate, 2 mg, propylene glycol 35% v/v. The pH is 6.0 (4.0 to 7.0). It is intended for the induction of general anesthesia by intravenous injection. The drug etomidate is chemically identified as (R)-(+)-ethyl-1-(1-phenylethyl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylate and has the following structural formula: Chemical Structure
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED AMIDATE™ (Etomidate Injection, USP) is supplied in single-dose containers as follows: Unit of Sale Concentration NDC 0409-6695-01 Tray of 10 Single-dose Fliptop Vials 20 mg/10 mL (2 mg/mL) NDC 0409-6695-02 Tray of 10 Single-dose Fliptop Vials 40 mg/20 mL (2 mg/mL) Store at 20 to 25°C (68 to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE AMIDATE is indicated by intravenous injection for the induction of general anesthesia. When considering use of AMIDATE, the usefulness of its hemodynamic properties (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ) should be weighed against the high frequency of transient skeletal muscle movements (see ADVERSE REACTIONS ). Intravenous AMIDATE is also indicated for the supplementation of subpotent anesthetic agents, such as nitrous oxide in oxygen, during maintenance of anesthesia for short operative procedures such as dilation and curettage or cervical conization.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Do not administer unless solution is clear and container is undamaged. Discard unused portion (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ). AMIDATE is intended for administration only by the intravenous route (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ). The dose for induction of anesthesia in adult patients and in pediatric patients above the age of ten (10) years will vary between 0.2 mg/kg and 0.6 mg/kg of body weight, and it must be individualized in each case. The usual dose for induction in these patients is 0.3 mg/kg, injected over a period of 30 to 60 seconds. There are inadequate data to make dosage recommendations for induction of anesthesia in patients below the age of ten (10) years; therefore, such use is not recommended. Geriatric patients may require reduced doses of etomidate. Smaller increments of intravenous AMIDATE may be administered to adult patients during short operative procedures to supplement subpotent anesthetic agents, such as nitrous oxide. The dosage employed under these circumstances, although usually smaller than the original induction dose, must be individualized. There are insufficient data to support this use of etomidate for longer adult procedures or for any procedures in pediatric patients; therefore, such use is not recommended. The use of intravenous fentanyl and other neuroactive drugs employed during the conduct of anesthesia may alter the etomidate dosage requirements. Consult the prescribing information for all other such drugs before using. Premedication AMIDATE is compatible with commonly administered pre-anesthetic medications, which may be employed as indicated. See also CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY , ADVERSE REACTIONS , and dosage recommendations for maintenance of anesthesia. AMIDATE anesthesia does not significantly alter the usual dosage requirements of neuromuscular blocking agents employed for endotracheal intubation or other purposes shortly after induction of anesthesia. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. To prevent needle-stick injuries, needles should not be recapped, purposely bent, or broken by hand.
