Drug Catalog - Product Detail
AMOXICILLIN CAP 500MG CP 500
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00143-9939-05 | HIKMA | 500 | 500MG | CAPSULE |
PACKAGE FILES

Generic Name
AMOXICILLIN
Substance Name
AMOXICILLIN
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA065291
Description
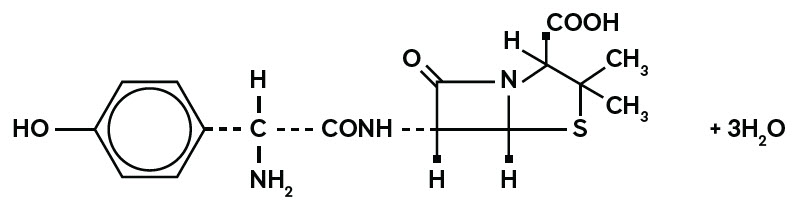
11 DESCRIPTION Amoxicillin, USP is a semisynthetic antibacterial (amoxicillin), an analog of ampicillin, with a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms. Chemically, it is (2 S ,5 R ,6 R )-6-[( R )-(-)-2-amino-2-( p -hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid trihydrate. It may be represented structurally as: The amoxicillin, USP molecular formula is C 16 H 19 N 3 O 5 S•3H 2 O, and the molecular weight is 419.45. Capsules: Each Amoxicillin Capsule, USP contains 250 mg or 500 mg amoxicillin as the trihydrate. The 250 mg capsule with caramel cap and ivory body is imprinted with West-ward 938, while the 500 mg capsule with ivory cap and ivory body is imprinted with West-ward 939. Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose Sodium, gelatin, magnesium stearate, titanium dioxide and yellow iron oxide. Additionally, the 250 mg capsules contain black iron oxide and red iron oxide. structural formula image
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Amoxicillin Capsules, USP 250 mg are available as caramel cap and ivory body. The cap of the 250 mg capsule is imprinted with West-ward and the body with 938. NDC 0143-9938-30: Bottle of 30 Capsules NDC 0143-9938-01: Bottle of 100 Capsules NDC 0143-9938-05: Bottle of 500 Capsules Amoxicillin Capsules, USP 500 mg are available as ivory cap and ivory body. The cap of the 500 mg capsule is imprinted with West-ward and the body with 939. NDC 0143-9939-20: Bottle of 20 Capsules NDC 0143-9939-01: Bottle of 100 Capsules NDC 0143-9939-05: Bottle of 500 Capsules Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F ) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required). Keep this and all medications out of the reach of children.
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Adults and Pediatric Patients Upper Respiratory Tract Infections of the Ear, Nose, and Throat: Amoxicillin capsules are indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible (ONLY β-lactamase–negative) isolates of Streptococcus species. (α-and β-hemolytic isolates only), Streptococcus pneumoniae , Staphylococcus spp. , or Haemophilus influenzae . Infections of the Genitourinary Tract : Amoxicillin capsules are indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible (ONLY β-lactamase–negative) isolates of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis , or Enterococcus faecalis . Infections of the Skin and Skin Structure: Amoxicillin capsules are indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible (ONLY β-lactamase–negative) isolates of Streptococcus spp. (α-and β-hemolytic isolates only), Staphylococcus spp., or E. coli. Infections of the Lower Respiratory Tract: Amoxicillin capsules are indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible (ONLY β-lactamase–negative) isolates of Streptococcus spp. (α-and β-hemolytic isolates only), S. pneumoniae, Staphylococcus spp., or H. influenzae . Adult Patients only • Helicobacter pylori Infection and Duodenal Ulcer Disease: Triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) with clarithromycin and lansoprazole : Amoxicillin, in combination with clarithromycin plus lansoprazole as triple therapy, is indicated for the treatment of patients with H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease (active or 1-year history of a duodenal ulcer) to eradicate H. pylori . Eradication of H. pylori has been shown to reduce the risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence. Dual therapy for H. pylori with lansoprazole : Amoxicillin, in combination with lansoprazole delayed-release capsules as dual therapy, is indicated for the treatment of patients with H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease (active or 1-year history of a duodenal ulcer) who are either allergic or intolerant to clarithromycin or in whom resistance to clarithromycin is known or suspected . (See the clarithromycin package insert, MICROBIOLOGY.) Eradication of H. pylori has been shown to reduce the risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence. Usage To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of amoxicillin and other antibacterial drugs, amoxicillin should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy. Amoxicillin is a penicillin-class antibacterial indicated for treatment of infections due to susceptible strains of designated microorganisms. ( 1 ) Adults and Pediatric Patients ( 1 ) Upper Respiratory Tract Infections of the Ear, Nose, and Throat. Infections of the Genitourinary Tract Infections of the Skin and Skin Structure Infections of the Lower Respiratory Tract Adult Patients only ( 1 ) Helicobacter pylori Infection and Duodenal Ulcer Disease Usage To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of amoxicillin capsules and other antibacterial drugs, amoxicillin capsules should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. ( 1 )
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION In Adults, 750 to 1750 mg/day in divided doses every 8 to 12 hours. In Pediatric Patients over 3 Months of Age, 20 to 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 to 12 hours. Refer to full prescribing information for specific dosing regimens. ( 2.2 , 2.3 ) The upper dose for neonates and infants aged 3 months or younger is 30 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hours. ( 2.3 ) Dosing for H. pylori Infection (in Adults): Triple therapy: 1 gram amoxicillin, 500 mg clarithromycin, and 30 mg lansoprazole, all given twice daily (every 12 hours) for 14 days. Dual therapy: 1 gram amoxicillin and 30 mg lansoprazole, each given three times daily (every 8 hours) for 14 days. ( 2.4 ) Reduce the dose in patients with severe renal impairment (GFR greater than 30 mL/min). ( 2.5 ) 2.1 Important Administration Instructions To minimize the potential for gastrointestinal intolerance, amoxicillin should be taken at the start of a meal. 2.2 Dosage for Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months (12 weeks) and Older Treatment should be continued for a minimum of 48 to 72 hours beyond the time that the patient becomes asymptomatic, or evidence of bacterial eradication has been obtained. It is recommended that there be at least 10 days’ treatment for any infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes to prevent the occurrence of acute rheumatic fever. In some infections, therapy may be required for several weeks. It may be necessary to continue clinical and/or bacteriological follow-up for several months after cessation of therapy. Table 1. Dosage Recommendations for Adult and Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months (12 weeks) and Older Infection Severity a Recommended Dosage for Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months and Older and Weight Greater than 40 kg Recommended Dosage for Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months and Older and Weight Less than 40 kg Ear/Nose/Throat Skin/ Skin Structure Genitourinary Tract Mild/ Moderate 500 mg every 12 hours or 250 mg every 8 hours 25 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 20 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours Severe 875 mg every 12 hours or 500 mg every 8 hours 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours Lower Respiratory Tract Mild/ Moderate or Severe 875 mg every 12 hours or 500 mg every 8 hours 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours or 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours a Dosage for infections caused by bacteria that are intermediate in their susceptibility to amoxicillin should follow the recommendations for severe infections. 2.3 Dosage in Pediatric Patients Aged Less than 12 Weeks (3 months) It is recommended that there be at least 10 days’ treatment for any infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes to prevent the occurrence of acute rheumatic fever. Due to incompletely developed renal function affecting elimination of amoxicillin in this age group, the recommended upper dose of amoxicillin is 30 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hours. There are currently no dosing recommendations for pediatric patients with impaired renal function. Treatment should be continued for a minimum of 48 to 72 hours beyond the time that the patient becomes asymptomatic, or evidence of bacterial eradication has been obtained. 2.4 Dosage for H. pylori Infection in Adults Triple therapy: The recommended adult oral dose is 1 gram amoxicillin, 500 mg clarithromycin, and 30 mg lansoprazole, all given twice daily (every 12 hours) for 14 days. Dual therapy: The recommended adult oral dose is 1 gram amoxicillin and 30 mg lansoprazole, each given three times daily (every 8 hours) for 14 days. Please refer to clarithromycin and lansoprazole full prescribing information. 2.5 Dosage in Renal Impairment for Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months and Older and Weight Greater than 40 kg Patients with impaired renal function do not generally require a reduction in dose unless the impairment is severe. Renal impairment patients with a glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 mL/min should NOT receive the 875 mg dose. See dosage regimens in patients with severe renal impairment provided in Table 2. Table 2. Dosing in Patients with Severe Renal Impairment Patients with Renal Impairment Dosage Regimen GFR 10 to 30 mL/min 500 mg or 250 mg every 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection GFR less than 10 mL/min 500 mg or 250 mg every 24 hours, depending on severity of the infection Hemodialysis 500 mg or 250 mg every 24 hours, depending on severity of the infection Administer an additional dose both during and at the end of dialysis
