Drug Catalog - Product Detail
Aripiprazole 15mg Tablet 30
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65162-0899-03 | AMNEAL PHARMACEUTICALS | 30 | 15MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES
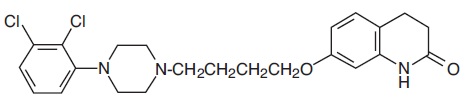






Generic Name
ARIPIPRAZOLE
Substance Name
ARIPIPRAZOLE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA204838
Description
11 DESCRIPTION Aripiprazole, USP is an atypical antipsychotic drug that is available as aripiprazole tablets, USP. Aripiprazole, USP is 7-[4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl]butoxy]-3,4-dihydrocarbostyril. The molecular formula is C 23 H 27 Cl 2 N 3 O 2 and its molecular weight is 448.38. The chemical structure is: Aripiprazole tablets, USP are available in 2 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, and 30 mg strengths. Inactive ingredients include croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and tartaric acid. The 2 mg and 5 mg tablets contain FD&C Blue No. 2 indigo carmine aluminum lake (30% to 36%). The 2 mg and 15 mg tablets contain ferric oxide yellow. The 10 mg and 30 mg tablets contain FD&C Red No. 40 allura red AC aluminum lake (15% to 17%). 1
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING 16.1 How Supplied Aripiprazole tablets USP, 2 mg, are supplied as green to light green colored, mosaic appearance, modified rectangle shaped, uncoated tablet with debossing “AN896” and “2” on one side and plain on the other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 30: NDC 65162-896-03 Bottles of 90: NDC 65162-896-09 Bottles of 500: NDC 65162-896-50 Bottles of 1000: NDC 65162-896-11 Aripiprazole tablets USP, 5 mg, are supplied as blue to light blue colored, mosaic appearance, modified rectangle shaped, uncoated tablet with debossing “AN897” and “5” on one side and plain on the other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 30: NDC 65162-897-03 Bottles of 90: NDC 65162-897-09 Bottles of 500: NDC 65162-897-50 Bottles of 1000: NDC 65162-897-11 Aripiprazole tablets USP, 10 mg, are supplied as pink to light pink colored, mosaic appearance, modified rectangle shaped, uncoated tablet with debossing “AN898” and “10” on one side and plain on the other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 30: NDC 65162-898-03 Bottles of 90: NDC 65162-898-09 Bottles of 500: NDC 65162-898-50 Bottles of 1000: NDC 65162-898-11 Aripiprazole tablets USP, 15 mg, are supplied as yellow to light yellow colored, mosaic appearance, round shaped, uncoated tablet with debossing “AN899” and “15” on one side and plain on the other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 30: NDC 65162-899-03 Bottles of 90: NDC 65162-899-09 Bottles of 500: NDC 65162-899-50 Bottles of 1000: NDC 65162-899-11 Aripiprazole tablets USP, 20 mg, are supplied as white to off-white, round shaped, uncoated tablet with debossing “AN901” and “20” on one side and plain on the other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 30: NDC 65162-901-03 Bottles of 90: NDC 65162-901-09 Bottles of 500: NDC 65162-901-50 Bottles of 1000: NDC 65162-901-11 Aripiprazole tablets USP, 30 mg, are supplied as pink to light pink colored, mosaic appearance, round shaped, uncoated tablet with debossing “AN902” and “30” on one side and plain on the other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 30: NDC 65162-902-03 Bottles of 90: NDC 65162-902-09 Bottles of 500: NDC 65162-902-50 Bottles of 1000: NDC 65162-902-11 16.2 Storage Tablets Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] in tightly closed containers.
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Aripiprazole Oral Tablets are indicated for the treatment of: Schizophrenia Irritability Associated with Autistic Disorder Treatment of Tourette’s Disorder Aripiprazole tablets are an atypical antipsychotic. The oral formulations are indicated for: Schizophrenia. ( 14.1 ) Irritability Associated with Autistic Disorder. ( 14.4 ) Treatment of Tourette’s disorder. ( 14.5 )
Dosage and Administration
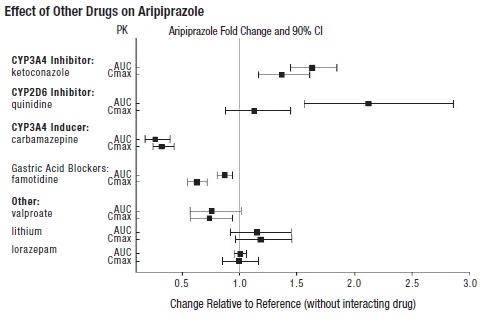
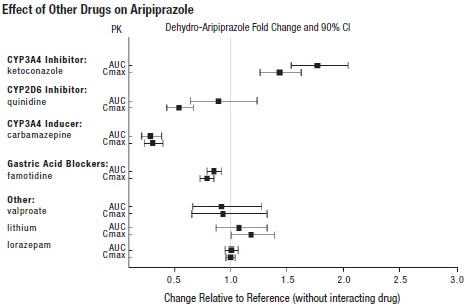
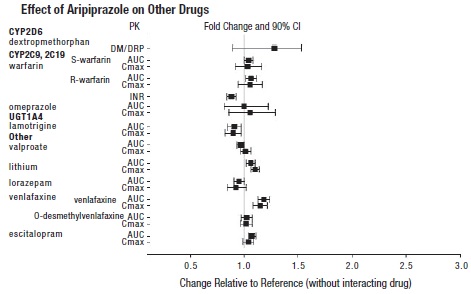
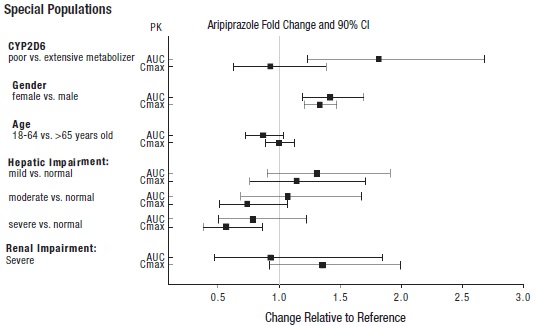
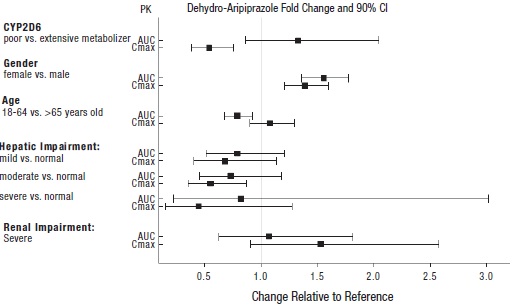
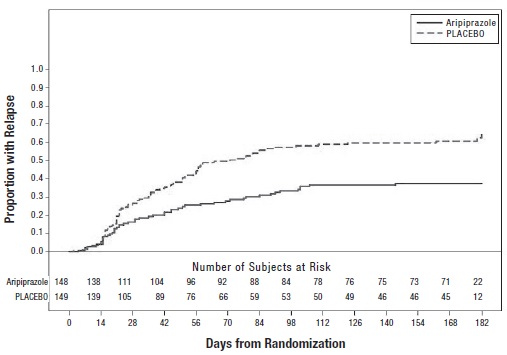
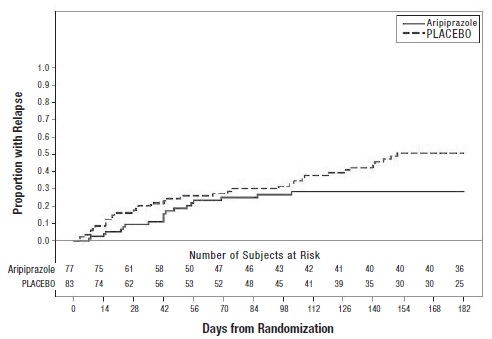
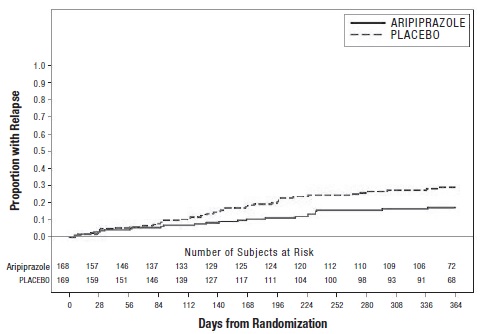
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Initial Dose Recommended Dose Maximum Dose Schizophrenia – adults (2.1) 10 to 15 mg/day 10 to 15 mg/day 30 mg/day Schizophrenia – adolescents (2.1) 2 mg/day 10 mg/day 30 mg/day Irritability associated with autistic disorder – pediatric patients (2.4) 2 mg/day 5 mg/day 10 mg/day Tourette’s disorder – (2.5) Patients <50 kg 2 mg/day 5 mg/day 10 mg/day Patients ≥50 kg 2 mg/day 10 mg/day 20 mg/day Oral formulations: Administer once daily without regard to meals. ( 2 ) Known CYP2D6 poor metabolizers: Half of the usual dose. ( 2.7 ) 2.1 Schizophrenia Adults The recommended starting and target dose for aripiprazole tablets is 10 mg/day or 15 mg/day administered on a once-a-day schedule without regard to meals. Aripiprazole tablets have been systematically evaluated and shown to be effective in a dose range of 10 mg/day to 30 mg/day, when administered as the tablet formulation; however, doses higher than 10 mg/day or 15 mg/day were not more effective than 10 mg/day or 15 mg/day. Dosage increases should generally not be made before 2 weeks, the time needed to achieve steady-state [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Maintenance Treatment: Maintenance of efficacy in schizophrenia was demonstrated in a trial involving patients with schizophrenia who had been symptomatically stable on other antipsychotic medications for periods of 3 months or longer. These patients were discontinued from those medications and randomized to either aripiprazole tablets 15 mg/day or placebo, and observed for relapse [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the continued need for maintenance treatment. Adolescents The recommended target dose of aripiprazole tablets is 10 mg/day. Aripiprazole was studied in adolescent patients 13 to 17 years of age with schizophrenia at daily doses of 10 mg and 30 mg. The starting daily dose of the tablet formulation in these patients was 2 mg, which was titrated to 5 mg after 2 days and to the target dose of 10 mg after 2 additional days. Subsequent dose increases should be administered in 5 mg increments. The 30 mg/day dose was not shown to be more efficacious than the 10 mg/day dose. Aripiprazole tablets can be administered without regard to meals [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the need for maintenance treatment. Switching from Other Antipsychotics There are no systematically collected data to specifically address switching patients with schizophrenia from other antipsychotics to aripiprazole tablets or concerning concomitant administration with other antipsychotics. While immediate discontinuation of the previous antipsychotic treatment may be acceptable for some patients with schizophrenia, more gradual discontinuation may be most appropriate for others. In all cases, the period of overlapping antipsychotic administration should be minimized. 2.4 Irritability Associated with Autistic Disorder Pediatric Patients (6 to 17 years) The recommended dosage range for the treatment of pediatric patients with irritability associated with autistic disorder is 5 mg/day to 15 mg/day. Dosing should be initiated at 2 mg/day. The dose should be increased to 5 mg/day, with subsequent increases to 10 mg/day or 15 mg/day if needed. Dose adjustments of up to 5 mg/day should occur gradually, at intervals of no less than one week [see Clinical Studies (14.4)] . Patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the continued need for maintenance treatment. 2.5 Tourette’s Disorder Pediatric Patients (6 to 18 years) The recommended dosage range for Tourette’s Disorder is 5 mg/day to 20 mg/day. For patients weighing less than 50 kg, dosing should be initiated at 2 mg/day with a target dose of 5 mg/day after 2 days. The dose can be increased to 10 mg/day in patients who do not achieve optimal control of tics. Dosage adjustments should occur gradually at intervals of no less than one week. For patients weighing 50 kg or more, dosing should be initiated at 2 mg/day for 2 days, and then increased to 5 mg/day for 5 days, with a target dose of 10 mg/day on Day 8. The dose can be increased up to 20 mg/day for patients who do not achieve optimal control of tics. Dosage adjustments should occur gradually in increments of 5 mg/day at intervals of no less than one week [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] . Patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the continued need for maintenance treatment. 2.7 Dosage Adjustments for Cytochrome P450 Considerations Dosage adjustments are recommended in patients who are known CYP2D6 poor metabolizers and in patients taking concomitant CYP3A4 inhibitors or CYP2D6 inhibitors or strong CYP3A4 inducers (see Table 2). When the co-administered drug is withdrawn from the combination therapy, aripiprazole tablets dosage should then be adjusted to its original level. When the co-administered CYP3A4 inducer is withdrawn, aripiprazole tablets dosage should be reduced to the original level over 1 to 2 weeks. Patients who may be receiving a combination of strong, moderate, and weak inhibitors of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 (e.g., a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor and a moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor or a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor with a moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor), the dosing may be reduced to one-quarter (25%) of the usual dose initially and then adjusted to achieve a favorable clinical response. Table 2: Dose Adjustments for Aripiprazole Tablets in Patients who are known CYP2D6 Poor Metabolizers and Patients Taking Concomitant CYP2D6 Inhibitors, 3A4 Inhibitors, and/or CYP3A4 Inducers Factors Dosage Adjustments for Aripiprazole Tablets Known CYP2D6 Poor Metabolizers Administer half of usual dose Known CYP2D6 Poor Metabolizers taking concomitant strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., itraconazole, clarithromycin) Administer a quarter of usual dose Strong CYP2D6 (e.g., quinidine, fluoxetine, paroxetine) or CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., itraconazole, clarithromycin) Administer half of usual dose Strong CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 inhibitors Administer a quarter of usual dose Strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin) Double usual dose over 1 to 2 weeks
