Drug Catalog - Product Detail
ATENOLOL W/CHLORTHALIDONE TB 100/25MG 100
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00591-5783-01 | ACTAVIS PHARMA | 100 | 100-25MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES
Generic Name
ATENOLOL AND CHLORTHALIDONE
Substance Name
ATENOLOL
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA073665
Description
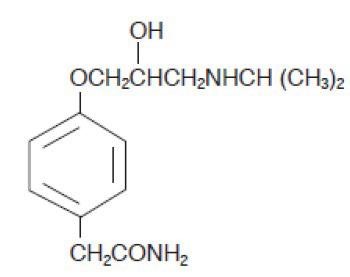
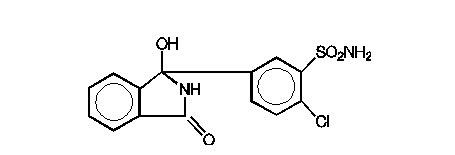
DESCRIPTION Atenolol and chlorthalidone tablets, USP are for the treatment of hypertension. It combines the antihypertensive activity of two agents: a beta 1 -selective (cardioselective) hydrophilic blocking agent (atenolol), and a monosulfonamyl diuretic (chlorthalidone). Atenolol, USP is Benzeneacetamide, 4-[2’-hydroxy-3’-[(1-methylethyl)amino]propoxy]-. It has the following structural formula: C 14 H 22 N 2 O 3 M.W. 266.34 Atenolol, USP (free base) is a relatively polar hydrophilic compound with a water solubility of 26.5 mg/mL at 37°C. It is freely soluble in 1N HCl (300 mg/mL at 25°C) and less soluble in chloroform (3 mg/mL at 25°C). Chlorthalidone, USP is 2-Chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1-isoindolinyl) benzene sulfonamide. Chlorthalidone, USP has a water solubility of 12 mg/100 mL at 20°C. It has the following structural formula: C 14 H 11 ClN 2 O 4 S M.W. 338.77 Each atenolol and chlorthalidone tablet, USP 50 mg/25 mg for oral administration contains: atenolol USP, 50 mg and chlorthalidone USP, 25 mg. Each atenolol and chlorthalidone tablet, USP 100 mg/25 mg for oral administration contains: atenolol USP, 100 mg and chlorthalidone USP, 25 mg. Atenolol and chlorthalidone tablets USP, 50 mg/25 mg and 100 mg/25 mg, contain the following inactive ingredients: magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone and sodium starch glycolate. 1 2
How Supplied
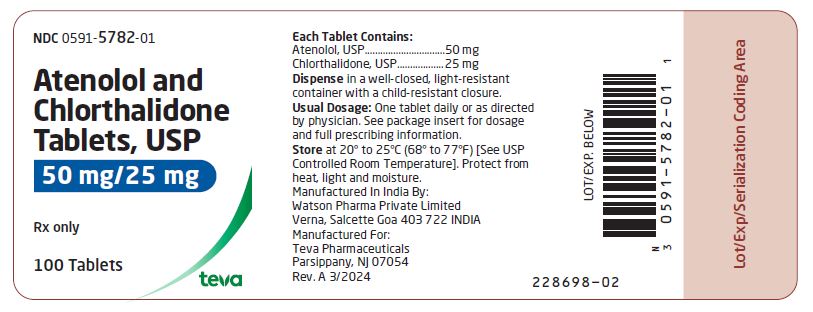
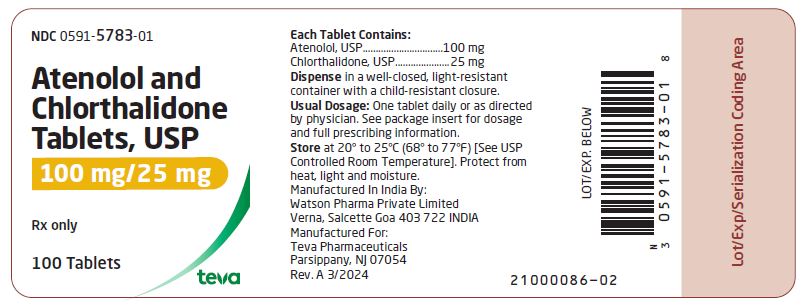
HOW SUPPLIED Atenolol and chlorthalidone tablets USP, 50 mg/25 mg are white, round, scored tablets imprinted with “DAN 5782” on one side and plain on the other side. Supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0591-5782-01). Atenolol and chlorthalidone tablets USP, 100 mg/25 mg are white, round tablets imprinted with “DAN 5783” on one side and plain on the other side. Supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0591-5783-01) Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a well-closed, light-resistant container with a child-resistant closure. Protect from heat, light and moisture. Manufactured In India By: Watson Pharma Private Limited Verna, Salcette Goa 403 722 INDIA Manufactured For: Teva Pharmaceuticals Parsippany, NJ 07054 Rev. A 3/2024
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Atenolol and chlorthalidone is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure lowers the risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes including atenolol and chlorthalidone. Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than 1 drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program’s Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC). Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly. Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal. Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy. This fixed dose combination drug is not indicated for initial therapy of hypertension. If the fixed dose combination represents the dose appropriate to the individual patient's needs, it may be more convenient than the separate components.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION DOSAGE MUST BE INDIVIDUALIZED. (See INDICATIONS AND USAGE . ) Chlorthalidone is usually given at a dose of 25 mg daily; the usual initial dose of atenolol is 50 mg daily. Therefore, the initial dose should be one atenolol and chlorthalidone 50 mg/25 mg tablet given once a day. If an optimal response is not achieved, the dosage should be increased to one atenolol and chlorthalidone 100 mg/25 mg tablet given once a day. When necessary, another antihypertensive agent may be added gradually beginning with 50 percent of the usual recommended starting dose to avoid an excessive fall in blood pressure. Since atenolol is excreted via the kidneys, dosage should be adjusted in cases of severe impairment of renal function. No significant accumulation of atenolol occurs until creatinine clearance falls below 35 mL/min/1.73 m 2 (normal range is 100 mL/min/1.73 m 2 to 150 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ); therefore, the following maximum dosages are recommended for patients with renal impairment. Creatinine Clearance Atenolol Elimination (mL/min/1.73m 2 ) Half-Life (hrs) Maximum Dosage 15-35 16-27 50 mg daily <15 >27 50 mg every other day
