Drug Catalog - Product Detail
ATOVAQUONE&PROGUANIL TAB 62.5/25MG 100CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68462-0402-01 | GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS | 100 | 62.5-25MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES



Generic Name
ATOVAQUONE AND PROGUANIL HYDROCHLORIDE PEDIATRIC
Substance Name
ATOVAQUONE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA091211
Description
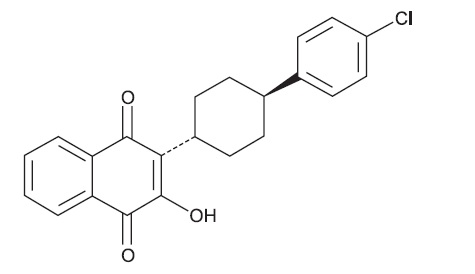
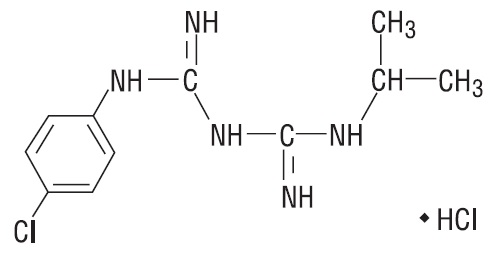
11 DESCRIPTION Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets (adult strength) and Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride pediatric tablets, for oral administration, contain a fixed-dose combination of the antimalarial agents atovaquone, USP and proguanil hydrochloride, USP. The chemical name of atovaquone, USP is trans -2-[4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexyl]-3-hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione. Atovaquone, USP is a yellow crystalline solid that is freely soluble in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone and in tetrahydrofuran; soluble in chloroform; sparingly soluble in acetone and dimethyl sulfoxide; slightly soluble in octanol, ethyl acetate, polyethylene glycol 200; very slightly soluble in 0.1N sodium hydroxide; insoluble in water. It has a molecular weight of 366.84 g/mol and the molecular formula C 22 H 19 ClO 3 . The compound has the following structural formula: The chemical name of proguanil hydrochloride, USP is 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-biguanide hydrochloride. Proguanil hydrochloride, USP is a white crystalline powder slightly soluble in water, sparingly soluble in alcohol, practically insoluble in methylene chloride. It has a molecular weight of 290.22 g/mol and the molecular formula C 11 H 16 ClN 5 •HCl. The compound has the following structural formula: Each atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablet (adult strength) contains 250 mg of atovaquone, USP and 100 mg of proguanil hydrochloride, USP and each atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride pediatric tablet contains 62.5 mg of atovaquone, USP and 25 mg of proguanil hydrochloride, USP. The inactive ingredients in the tablets are colloidal silicon dioxide, ferric oxide red, hypromellose 2910, low substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, poloxamer 188, polyethylene glycol 400, polyethylene glycol 8000, povidone K30, sodium starch glycolate and titanium dioxide. atovaquonestructure proguanilstructure
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets, containing 250 mg atovaquone, USP and 100 mg proguanil hydrochloride, USP are pinkish brown to brown colored, circular, biconvex beveled edge, film-coated tablets with ‘404’ debossed on one side and ‘G’ debossed on the other side. Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets 250 mg / 100 mg NDC 68462-404-01 bottles of 100 tablets NDC 68462-404-67 Carton of 24 tablets (2 x 12 unit-dose). Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride pediatric tablets, containing 62.5 mg atovaquone, USP and 25 mg proguanil hydrochloride, USP are pinkish brown to brown colored, circular, biconvex beveled edged, film coated tablets with ‘70’ debossed on one side and ‘G’ debossed on the other side. Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride pediatric tablets 62.5 mg / 25 mg NDC 68462-402-01 bottles of 100 tablets. Storage Conditions Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets are an antimalarial indicated for: • prophylaxis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria, including in areas where chloroquine resistance has been reported. ( 1.1 ) • treatment of acute, uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria. ( 1.2 ) 1.1 Prevention of Malaria Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the prophylaxis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria, including in areas where chloroquine resistance has been reported. 1.2 Treatment of Malaria Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the treatment of acute, uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria. Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets have been shown to be effective in regions where the drugs chloroquine, halofantrine, mefloquine, and amodiaquine may have unacceptable failure rates, presumably due to drug resistance.
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION The daily dose should be taken at the same time each day with food or a milky drink. In the event of vomiting within 1 hour after dosing, a repeat dose should be taken. Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets may be crushed and mixed with condensed milk just prior to administration to patients who may have difficulty swallowing tablets. • Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets should be taken with food or a milky drink. Prophylaxis ( 2.1 ): • Start prophylaxis 1 or 2 days before entering a malaria-endemic area and continue daily during the stay and for 7 days after return. • Adults: One adult strength tablet per day. • Pediatric Patients: Dosage based on body weight (see Table 1). Treatment ( 2.2 ): • Adults: Four adult strength tablets as a single daily dose for 3 days. • Pediatric Patients: Dosage based on body weight (see Table 2). Renal Impairment ( 2.3 ): • Do not use for prophylaxis of malaria in patients with severe renal impairment. • Use with caution for treatment of malaria in patients with severe renal impairment. 2.1 Prevention of Malaria Start prophylactic treatment with atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets 1 or 2 days before entering a malaria-endemic area and continue daily during the stay and for 7 days after return. Adults One atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablet (adult strength = 250 mg atovaquone/100 mg proguanil hydrochloride) per day. Pediatric Patients The dosage for prevention of malaria in pediatric patients is based upon body weight (Table 1). Table 1. Dosage for Prevention of Malaria in Pediatric Patients Weight (kg) Atovaquone/ Proguanil HCl Total Daily Dose Dosage Regimen 11 to 20 62.5 mg/25 mg 1 Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride pediatric tablet daily 21 to 30 125 mg/50 mg 2 Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride pediatric tablets as a single daily dose 31 to 40 187.5 mg/75 mg 3 Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride pediatric tablets as a single daily dose > 40 250 mg/100 mg 1 Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablet (adult strength) as a single daily dose 2.2 Treatment of Acute Malaria Adults Four atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets (adult strength; total daily dose 1 g atovaquone/400 mg proguanil hydrochloride) as a single daily dose for 3 consecutive days. Pediatric Patients The dosage for treatment of acute malaria in pediatric patients is based upon body weight (Table 2). Table 2. Dosage for Treatment of Acute Malaria in Pediatric Patients Weight (kg) Atovaquone/ Proguanil HCl Total Daily Dose Dosage Regimen 5 to 8 125 mg/50 mg 2 Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride pediatric tablets daily for 3 consecutive days 9 to 10 187.5 mg/75 mg 3 Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride pediatric tablets daily for 3 consecutive days 11 to 20 250 mg/100 mg 1 Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablet (adult strength) daily for 3 consecutive days 21 to 30 500 mg/200 mg 2 Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets (adult strength) as a single daily dose for 3 consecutive days 31 to 40 750 mg/300 mg 3 Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets (adult strength) as a single daily dose for 3 consecutive days >40 1 g/400 mg 4 Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets (adult strength) as a single daily dose for 3 consecutive days 2.3 Renal Impairment Do not use atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride tablets for malaria prophylaxis in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min) [see Contraindications ( 4 )] . Use with caution for the treatment of malaria in patients with severe renal impairment, only if the benefits of the 3 day treatment regimen outweigh the potential risks associated with increased drug exposure. No dosage adjustments are needed in patients with mild (creatinine clearance 50 to 80 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance 30 to 50 mL/min) renal impairment. [See Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )].
