Drug Catalog - Product Detail
Bisoprolol & Hydrochlorothiazide Tab 10-6.25 MG 30 EA
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 42799-0922-30 | EDENBRIDGE PHARMACEUTICALS | 30 | 10-6.25MG | NA |
PACKAGE FILES












Generic Name
BISOPROLOL FUMARATE AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE
Substance Name
BISOPROLOL FUMARATE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA212678
Description
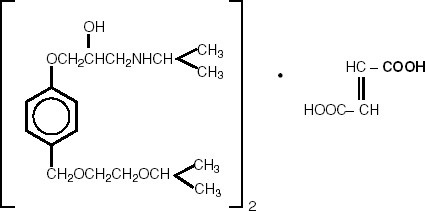
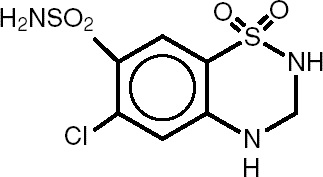
DESCRIPTION Bisoprolol Fumarate and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets, USP Rx only Revised January 2024 DESCRIPTION Bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets, USP, are indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It combines two antihypertensive agents in a once-daily dosage: a synthetic beta 1 -selective (cardioselective) adrenoceptor blocking agent (bisoprolol fumarate) and a benzothiadiazine diuretic (hydrochlorothiazide). Bisoprolol fumarate is chemically described as (±)-1-[4-[[2-(1 methylethoxy)ethoxy]methyl] phenoxy]-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-2-propanol( E )-2-butenedioate (2:1) (salt). It possesses an asymmetric carbon atom in its structure and is provided as a racemic mixture. The S(-) enantiomer is responsible for most of the beta-blocking activity. Its empirical formula is (C 18 H 31 NO 4 ) 2 •C 4 H 4 O 4 and it has a molecular weight of 766.97. Its structural formula is: Bisoprolol fumarate is a white crystalline powder, approximately equally hydrophilic and lipophilic, and readily soluble in water, methanol, ethanol, and chloroform. Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) is 6-Chloro-3,4-dihydro-2 H -1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide. It is a white, or practically white, practically odorless crystalline powder. It is slightly soluble in water, sparingly soluble in dilute sodium hydroxide solution, freely soluble in n-butylamine and dimethylformamide, sparingly soluble in methanol, and insoluble in ether, chloroform, and dilute mineral acids. Its empirical formula is C 7 H 8 ClN 3 O 4 S 2 and it has a molecular weight of 297.73. Its structural formula is: Each bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablet 2.5 mg/6.25 mg for oral administration contains: Bisoprolol fumarate....................................................... 2.5 mg Hydrochlorothiazide….................................................... 6.25 mg Each bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablet 5 mg/6.25 mg for oral administration contains: Bisoprolol fumarate...................................................…. 5 mg Hydrochlorothiazide….................................................... 6.25 mg Each bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablet 10 mg/6.25 mg for oral administration contains: Bisoprolol fumarate...................................................... 10 mg Hydrochlorothiazide….................................................... 6.25 mg Inactive ingredients include Anhydrous Lactose, Crospovidone, Hypromellose, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Polyethylene Glycol, Polysorbate 80, Pregelatinized Starch, Stearic Acid, and Titanium Dioxide. The 5 mg/6.25 mg tablet also contains D&C Red #30. The 2.5 mg/6.25 mg tablet also contains D&C Yellow #10 Aluminum Lake and FD&C Yellow #6. BISO API Structure HCTZ API Structure
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets, 2.5 mg/6.25 mg: Yellow, round, biconvex, film-coated, unscored tablets, debossed with “920” on one side and plain on the reverse side, supplied as follows: Bottle of 30 Tablets NDC 42799-920-30 Bottle of 100 Tablets NDC 42799-920-01 Bottle of 500 Tablets NDC 42799-920-02 Bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets, 5 mg/6.25 mg: Pink, round, biconvex, film-coated, unscored tablets, debossed with “921” on one side and plain on the reverse side, supplied as follows: Bottle of 30 Tablets NDC 42799-921-30 Bottle of 100 Tablets NDC 42799-921-01 Bottle of 500 Tablets NDC 42799-921-02 Bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets, 10 mg/6.25 mg: White to off-white, round, biconvex, film-coated, unscored tablets, debossed with “922” on one side and plain on the reverse side, supplied as follows: Bottle of 30 Tablets NDC 42799-922-30 Bottle of 100 Tablets NDC 42799-922-01 Bottle of 500 Tablets NDC 42799-922-02 Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tight container. Edenbridge Pharmaceuticals, LLC Parsippany, New Jersey, 07054 Revised January 2024
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS & USAGE Bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets are indicated in the management of hypertension.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION Bisoprolol is an effective treatment of hypertension in once-daily doses of 2.5 to 40 mg, while hydrochlorothiazide is effective in doses of 12.5 to 50 mg. In clinical trials of bisoprolol/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy using bisoprolol doses of 2.5 to 20 mg and hydrochlorothiazide doses of 6.25 to 25 mg, the antihypertensive effects increased with increasing doses of either component. The adverse effects (see WARNINGS ) of bisoprolol are a mixture of dose-dependent phenomena (primarily bradycardia, diarrhea, asthenia, and fatigue) and dose-independent phenomena (eg, occasional rash); those of hydrochlorothiazide are a mixture of dose-dependent phenomena (primarily hypokalemia) and dose-independent phenomena (eg, possibly pancreatitis); the dose- dependent phenomena for each being much more common than the dose-independent phenomena. The latter consist of those few that are truly idiosyncratic in nature or those that occur with such low frequency that a dose relationship may be difficult to discern. Therapy with a combination of bisoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide will be associated with both sets of dose- independent adverse effects, and to minimize these, it may be appropriate to begin combination therapy only after a patient has failed to achieve the desired effect with monotherapy. On the other hand, regimens that combine low doses of bisoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide should produce minimal dose-dependent adverse effects, eg, bradycardia, diarrhea, asthenia and fatigue, and minimal dose-dependent adverse metabolic effects, ie, decreases in serum potassium (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ). Therapy Guided by Clinical Effect A patient whose blood pressure is not adequately controlled with 2.5-20 mg bisoprolol daily may instead be given bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets. Patients whose blood pressures are adequately controlled with 50 mg of hydrochlorothiazide daily, but who experience significant potassium loss with this regimen, may achieve similar blood pressure control without electrolyte disturbance if they are switched to bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets. Initial Therapy Antihypertensive therapy may be initiated with the lowest dose of bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets, one 2.5/6.25 mg tablet once daily. Subsequent titration (14 day intervals) may be carried out with bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets up to the maximum recommended dose 20/12.5 mg (two 10/6.25 mg tablets) once daily, as appropriate. Replacement Therapy The combination may be substituted for the titrated individual components. Cessation of Therapy If withdrawal of bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets therapy is planned, it should be achieved gradually over a period of about 2 weeks. Patients should be carefully observed. Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment: As noted in the WARNINGS section, caution must be used in dosing/titrating patients with hepatic impairment or renal dysfunction. Since there is no indication that hydrochlorothiazide is dialyzable, and limited data suggest that bisoprolol is not dialyzable, drug replacement is not necessary in patients undergoing dialysis. Geriatric Patients: Dosage adjustment on the basis of age is not usually necessary, unless there is also significant renal or hepatic dysfunction (see above and WARNINGS section). Pediatric Patients: There is no pediatric experience with bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide tablets.
