Drug Catalog - Product Detail
Bosentan 125mg Tablets 60
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65162-0874-06 | AMNEAL PHARMACEUTICALS | 60 | 125MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES


Generic Name
BOSENTAN
Substance Name
BOSENTAN ANHYDROUS
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA209742
Description
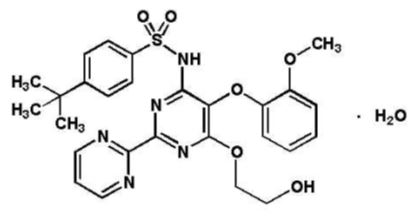
11 DESCRIPTION Bosentan is an endothelin receptor antagonist that belongs to a class of highly substituted pyrimidine derivatives, with no chiral centers. It is designated chemically as 4-tert-butyl-N-[6-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-5-(2-methoxy-phenoxy)-[2,2´]-bipyrimidin-4-yl]- benzenesulfonamide monohydrate and has the following structural formula: Bosentan has a molecular weight of 569.64 and a molecular formula of C 27 H 29 N 5 O 6 S•H 2 O. Bosentan is a white to yellowish powder. It is poorly soluble in water (1 mg/100 mL) and in aqueous solutions at low pH (0.1 mg/100 mL at pH 1.1 and 4.0; 0.2 mg/100 mL at pH 5.0). Solubility increases at higher pH values (43 mg/100 mL at pH 7.5). In the solid state, bosentan is very stable, is not hygroscopic and is not light sensitive. Bosentan tablets are available as 62.5 mg and 125 mg film-coated tablets for oral administration, and contain the following excipients: corn starch, ethyl cellulose, glyceryl behenate, hypromellose, iron oxide yellow, iron oxide red, magnesium stearate, pregelatinized starch, povidone, sodium starch glycolate type A, titanium dioxide, triacetin and talc. Each bosentan 62.5 mg tablet contains 64.541 mg of bosentan monohydrate, equivalent to 62.5 mg of anhydrous bosentan. Each bosentan 125 mg tablet contains 129.082 mg of bosentan monohydrate, equivalent to 125 mg of anhydrous bosentan. 10
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Bosentan Tablets, 62.5 mg are supplied as orange, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with “AN” on one side and “873” on the other side, packaged in a white high-density polyethylene bottle and a white polypropylene child-resistant cap. They are available as: Bottles of 60: NDC 65162-873-06 Bosentan Tablets, 125 mg are supplied as orange, oval, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with “AN” on one side and “874” on the other side, packaged in a white high-density polyethylene bottle and a white polypropylene child-resistant cap. They are available as: Bottles of 60: NDC 65162-874-06 Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep out of the reach of children.
Indications & Usage
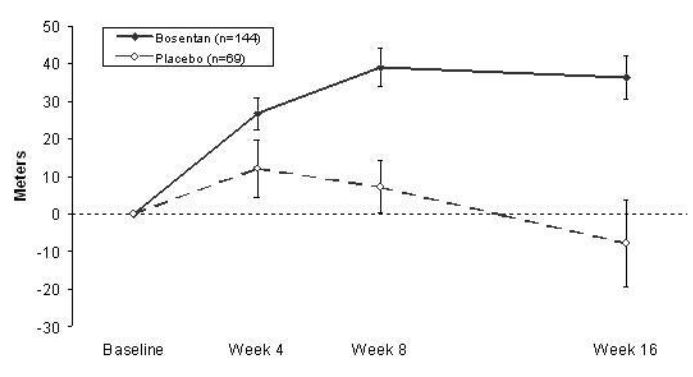
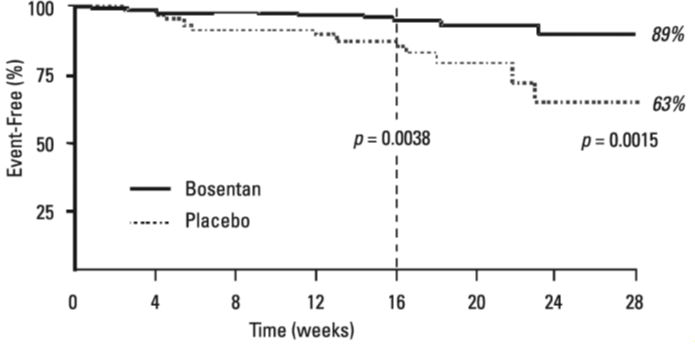
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Bosentan tablets are indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1): in adults to improve exercise ability and to decrease clinical worsening. Studies establishing effectiveness included predominantly patients with WHO Functional Class II-IV symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (60%), PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (21%), and PAH associated with congenital heart disease with left-to-right shunts (18%) [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Bosentan is an endothelin receptor antagonist indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1): in adults to improve exercise ability and to decrease clinical worsening. Studies establishing effectiveness included predominantly patients with WHO Functional Class II-IV symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (60%), PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (21%), and PAH associated with congenital heart disease with left-to-right shunts (18%). ( 1 )
Dosage and Administration
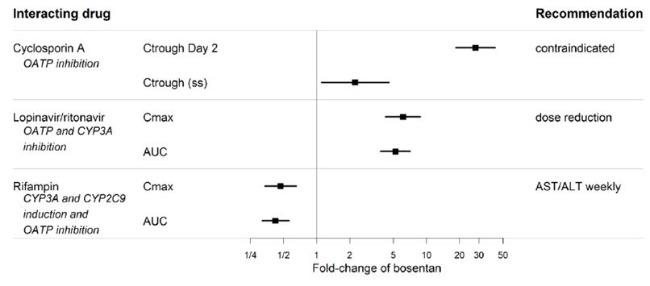
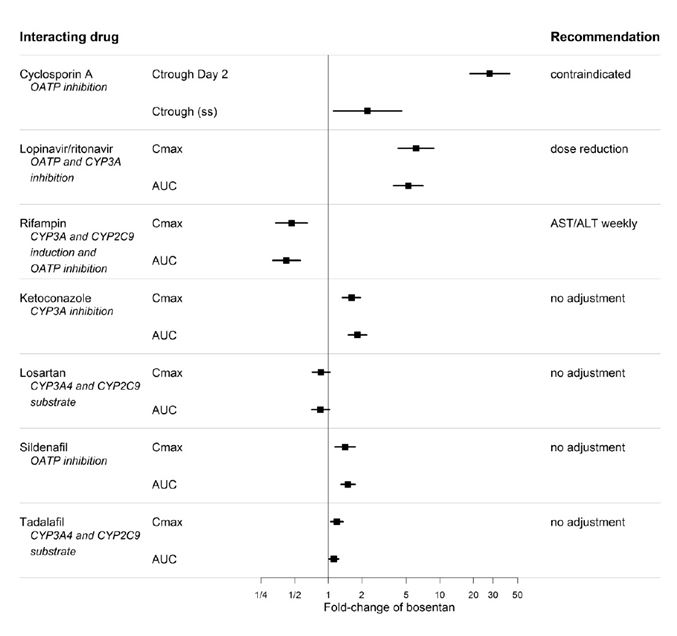
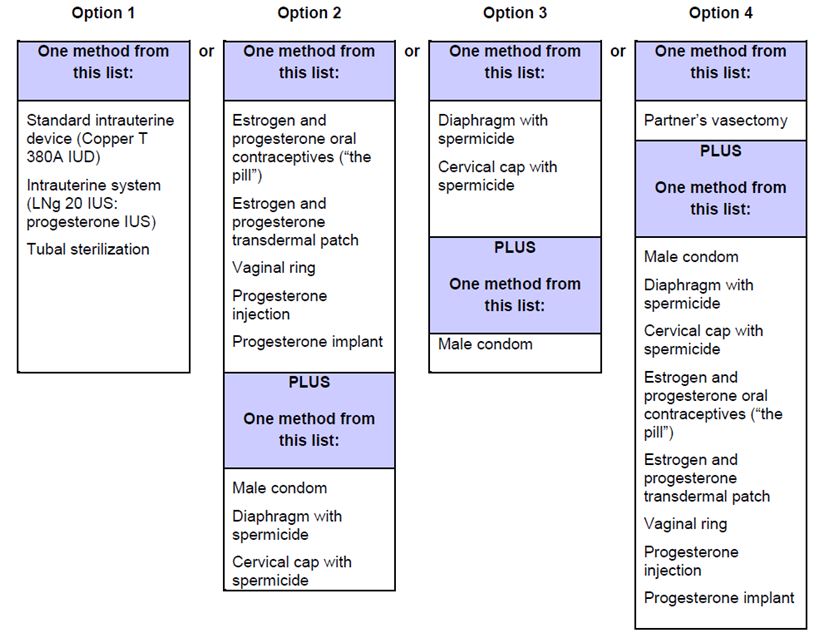
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Patients older than 12 years of age: initiate at 62.5 mg orally twice daily; for patients weighing greater than 40 kg, increase to 125 mg orally twice daily after 4 weeks. ( 2.2 ) Reduce the dose and closely monitor patients developing aminotransferase elevations more than 3 × Upper Limit of Normal (ULN). ( 2.1 ) 2.1 Required Monitoring Healthcare professionals who prescribe bosentan tablets must enroll in the Bosentan REMS Program and must comply with the required monitoring to minimize the risks associated with bosentan tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]. Obtain a pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential prior to bosentan tablets treatment, monthly during treatment and one month after stopping bosentan tablets. Initiate treatment with bosentan tablets in females of reproductive potential only after a negative pregnancy test [see Boxed Warning , Contraindications (4.1) , Warnings and Precautions (5.3) , Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 )] . Measure liver aminotransferase levels prior to initiation of treatment and then monthly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] . 2.2 Recommended Dosage Administer bosentan tablets orally following the dosing recommendations in Table 1. Doses above 125 mg twice daily did not appear to confer additional benefit sufficient to offset the increased risk of hepatotoxicity. Table 1: Dosing Recommendations Initial 4 weeks Maintenance (after 4 weeks) Patients > 12 years of age and > 40 kg 62.5 mg twice daily 125 mg twice daily Patients > 12 years of age and < 40 kg 62.5 mg twice daily 62.5 mg twice daily 2.3 Administration Bosentan film-coated tablets should be administered orally twice daily. 2.4 Dosage Adjustments for Aminotransferase Elevations If aminotransferase levels increase, adjust monitoring and treatment plan according to Table 2. Discontinue bosentan tablets if liver aminotransferase elevations are accompanied by clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity (such as nausea, vomiting, fever, abdominal pain, jaundice, or unusual lethargy or fatigue) or bilirubin ≥ 2 x Upper Limit of Normal (ULN). There is no experience with the reintroduction of bosentan tablets in these circumstances. Table 2: Dosage Adjustment and Monitoring in Patients Developing Aminotransferase Elevations > 3 x ULN ALT/AST levels Treatment and monitoring recommendations > 3 and ≤ 5 x ULN Confirm by another aminotransferase test; if confirmed, in patients > 12 years and > 40 kg , reduce the daily dose to 62.5 mg twice daily or interrupt treatment, and monitor aminotransferase levels at least every 2 weeks. If the aminotransferase levels return to pretreatment values, treatment may continue or be reintroduced at 62.5 mg twice daily, with reassessment of aminotransferase levels within 3 days. in patients > 12 years and < 40 kg , interrupt treatment with no prior dose reduction. If the aminotransferase levels return to pretreatment values, reintroduce at the dose used prior to treatment interruption, with reassessment of aminotransferase levels within 3 days. > 5 and ≤ 8 x ULN Confirm by another aminotransferase test; if confirmed, stop treatment and monitor aminotransferase levels at least every 2 weeks. Once the aminotransferase levels return to pretreatment values, in patients > 12 years , consider reintroduction of treatment at 62.5 mg twice daily, with reassessment of aminotransferase levels within 3 days. > 8 x ULN Stop treatment permanently. There is no experience with reintroduction of Bosentan in these circumstances. 2.5 Use with Ritonavir Co-administration of Bosentan Tablets in Patients on Ritonavir In patients who have been receiving ritonavir for at least 10 days, start bosentan tablets at the recommended initial dose once daily or every other day based upon individual tolerability [see Cytochrome P450 Drug Interactions (7.1) ] . Co-administration of Ritonavir in Patients on Bosentan Tablets Discontinue use of bosentan tablets at least 36 hours prior to initiation of ritonavir. After at least 10 days following the initiation of ritonavir, resume bosentan tablets at the recommended initial dose once daily or every other day based upon individual tolerability [see Cytochrome P450 Drug Interactions (7.1) ] . 2.6 Use in Patients with Pre-existing Hepatic Impairment Avoid initiation of bosentan tablets in patients with aminotransferases > 3 x ULN. No dose adjustment is required in patients with mildly impaired liver function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) , Use in Specific Populations (8.6) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
