Drug Catalog - Product Detail
BUSPIRONE HCL TAB 5MG 100CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16729-0200-01 | ACCORD HEALTHCARE | 100 | 5MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES




Generic Name
BUSPIRONE HYDROCHLORIDE
Substance Name
BUSPIRONE HYDROCHLORIDE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA202557
Description
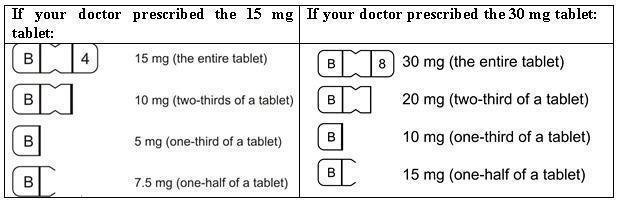
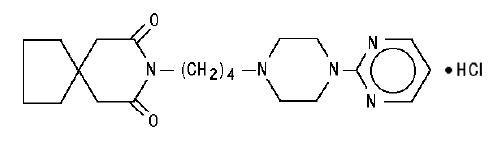
DESCRIPTION Buspirone hydrochloride tablets, USP are an antianxiety agent that is not chemically or pharmacologically related to the benzodiazepines, barbiturates, or other sedative/anxiolytic drugs. Buspirone hydrochloride is a white crystalline, water soluble compound with a molecular weight of 422.0. Chemically, buspirone hydrochloride is 8 -[4-[4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyl]8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione monohydrochloride. The empirical formula C 21 H 31 N 5 O 2 • HCl is represented by the following structural formula: Buspirone hydrochloride is supplied as tablets for oral administration contains 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg or 30 mg of buspirone hydrochloride, USP. The 5 mg, 7.5 mg Note :- Not applicable for divided doses and 10 mg tablets are scored so they can be bisected. Thus, the 5 mg tablet can also provide a 2.5 mg dose, and the 10-mg tablet can provide a 5 mg dose. The 15 mg tablets are scored such that they may be bisected or trisected. Thus, a single tablet can provide the following doses: 15 mg (entire tablet), 10 mg (two-thirds of a tablet), 7.5 mg (one-half of a tablet) or 5 mg (one-third of a tablet). The 30 mg tablets are scored such that they may be bisected or trisected. Thus, a single tablet can provide the following doses: 30 mg (entire tablet), 20 mg (two-thirds of a tablet), 15 mg (one-half of a tablet), or 10 mg (one-third of a tablet). Buspirone hydrochloride tablets USP contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium starch glycolate (Type A - potato starch). Buspirone structural formula
How Supplied
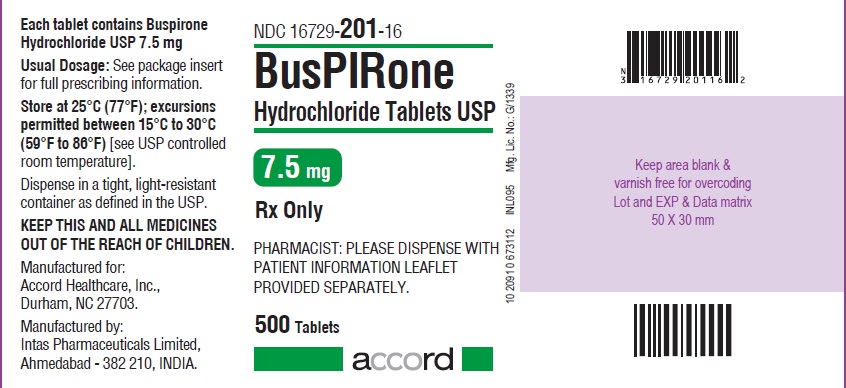
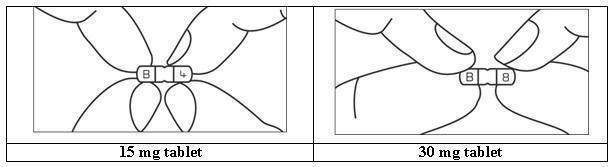
HOW SUPPLIED BusPIRone Hydrochloride Tablets, USP 5 mg are available as white colored, ovoid rectangular shape, biconvex, uncoated tablets, debossed with “B” and “1” on either side of breakline on one side and another side is plain containing 5 mg buspirone hydrochloride (NDC 16729-200), packaged in bottles of 100 tablets (NDC 16729-200-01), 500 tablets (NDC 16729- 200-16) and 1,000 tablets (NDC 16729-200-17). BusPIRone Hydrochloride Tablets, USP 7.5 mg are available as white colored, ovoid rectangular shape, biconvex, uncoated tablets, debossed with “B” and “2” on either side of breakline on one side and another side is plain containing 7.5 mg buspirone hydrochloride (NDC 16729- 201), packaged in bottles of 100 tablets (NDC 16729-201-01), 500 tablets(NDC 16729- 201-16) and 1,000 tablets (NDC 16729-201-17). BusPIRone Hydrochloride Tablets, USP 10 mg are available as white colored, ovoid rectangular shape, biconvex, uncoated tablet, debossed with “B” and “3” on either side of breakline on one side and another side is plain containing 10 mg buspirone hydrochloride (NDC 16729-202), packaged in bottles of 100 tablets (NDC 16729-202-01), 500 tablets (NDC 16729-202- 16) and 1,000 tablets (NDC 16729-202-17). BusPIRone Hydrochloride Tablets, USP 15 mg are available as white colored, rectangle shape, beveled edge, uncoated tablets, debossed with two breaklines in between “B” and “4” on one side, another side is plain with two breaklines and having one breakline on side surface containing 15 mg buspirone hydrochloride (NDC 16729-203). These tablets are scored to provide 15 mg (entire tablet), 10 mg (two- third of a tablet), 7.5 mg (one-half of a tablet) or 5 mg (one third of a tablet) are packaged in bottles of 60 tablets (NDC 16729-203-12), 100 tablets (NDC 16729-203-01), 180 tablets (NDC 16729-203-59), 500 tablets (NDC 16729-203-16) and 1,000 tablets (NDC 16729-203-17). BusPIRone Hydrochloride Tablets, USP 30 mg are available as white colored, rectangle shape, beveled edge, uncoated tablets, debossed with two breaklines in between “B” & “8” on one side, another side is plain with two breaklines and having one breakline on side surface containing 30 mg buspirone hydrochloride (NDC 16729-289), these tablets are scored to provide 30 mg (entire tablet), 20 mg (two- thirds of a tablet), 15 mg (one-half of a tablet) or 10 mg (one-third of a tablet) are packaged in bottles of 60 tablets (NDC 16729- 289-12), 100 tablets (NDC 16729-289-01), 180 tablets (NDC 16729-289-59), 500 tablets (NDC 16729-289-16) and 1,000 tablets (NDC 16729-289-17). PHARMACIST: Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required). Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted between 15° C to 30° C (59° F to 86° F) [see USP controlled room temperature]. KEEP THIS AND ALL OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Buspirone hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the management of anxiety disorders or the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety. Anxiety or tension associated with the stress of everyday life usually does not require treatment with an anxiolytic. The efficacy of buspirone hydrochloride tablets has been demonstrated in controlled clinical trials of outpatients whose diagnosis roughly corresponds to Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD). Many of the patients enrolled in these studies also had coexisting depressive symptoms and buspirone hydrochloride tablets relieved anxiety in the presence of these coexisting depressive symptoms. The patients evaluated in these studies had experienced symptoms for periods of 1 month to over 1 year prior to the study, with an average symptom duration of 6 months. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (300.02) is described in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, III 1 as follows: Generalized, persistent anxiety (of at least 1 month continual duration), manifested by symptoms from three of the four following categories: Motor tension: shakiness, jitteriness, jumpiness, trembling, tension, muscle aches, fatigability, inability to relax, eyelid twitch, furrowed brow, strained face, fidgeting, restlessness, easy startle. Autonomic hyperactivity: sweating, heart pounding or racing, cold, clammy hands, dry mouth, dizziness, lightheadedness, paresthesias (tingling in hands or feet), upset stomach, hot or cold spells, frequent urination, diarrhea, discomfort in the pit of the stomach, lump in the throat, flushing, pallor, high resting pulse, and respiration rate. Apprehensive expectation: anxiety, worry, fear, rumination, and anticipation of misfortune to self or others. Vigilance and scanning: hyperattentiveness resulting in distractibility, difficulty in concentrating, insomnia, feeling "on edge," irritability, impatience. The above symptoms would not be due to another mental disorder, such as a depressive disorder or schizophrenia. However, mild depressive symptoms are common in GAD. The effectiveness of buspirone hydrochloride tablets in long-term use, that is, for more than 3 to 4 weeks, has not been demonstrated in controlled trials. There is no body of evidence available that systematically addresses the appropriate duration of treatment for GAD. However, in a study of long-term use, 264 patients were treated with buspirone hydrochloride tablets for 1 year without ill effect. Therefore, the physician who elects to use buspirone hydrochloride tablets for extended periods should periodically reassess the usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION The recommended initial dose is 15 mg daily (7.5 mg b.i.d.). To achieve an optimal therapeutic response, at intervals of 2 to 3 days the dosage may be increased 5 mg per day, as needed. The maximum daily dosage should not exceed 60 mg per day. In clinical trials allowing dose titration, divided doses of 20 mg to 30 mg per day were commonly employed. The bioavailability of buspirone is increased when given with food as compared to the fasted state (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ). Consequently, patients should take buspirone in a consistent manner with regard to the timing of dosing; either always with or always without food. When buspirone is to be given with a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4, the dosage recommendations described in the PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions section should be followed. Switching a Patient To or From a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) Antidepressant At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAOI intended to treat depression and initiation of therapy with buspirone hydrochloride tablets. Conversely, at least 14 days should be allowed after stopping buspirone hydrochloride tablets before starting an MAOI antidepressant CONTRAINDICATIONS and DRUG INTERACTIONS ). Use of Buspirone Hydrochloride Tablets with (Reversible) MAOIs, Such as Linezolid or Methylene Blue Do not start buspirone hydrochloride tablets in a patient who is being treated with a reversible MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue because there is an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. In a patient who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition, non-pharmacological interventions, including hospitalization, should be considered [see CONTRAINDICATIONS and DRUG INTERACTIONS ). In some cases, a patient already receiving therapy with buspirone hydrochloride tablets may require urgent treatment with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. If acceptable alternatives to linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are not available and the potential benefits of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are judged to outweigh the risks of serotonin syndrome in a particular patient, buspirone hydrochloride tablets should be stopped promptly, and linezolid or intravenous methylene blue can be administered. The patient should be monitored for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for 2 weeks or until 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, whichever comes first. Therapy with buspirone hydrochloride tablets may be resumed 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue (see WARNINGS ). The risk of administering methylene blue by non-intravenous routes (such as oral tablets or by local injection) or in intravenous doses much lower than 1 mg per kg with buspirone hydrochloride tablets is unclear. The clinician should, nevertheless, be aware of the possibility of emergent symptoms of serotonin syndrome with such use (see CONTRAINDICATIONS , WARNINGS and DRUG INTERACTIONS ).
