Drug Catalog - Product Detail
CALCITRIOL ORAL SOLUTION SUSP 1MCG/ML 15ML
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 63304-0241-59 | SUN PHARMACEUTICALS | 15 | 1MCG/ML | SOLUTION |
PACKAGE FILES


Generic Name
CALCITRIOL
Substance Name
CALCITRIOL
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
NDA018044
Description
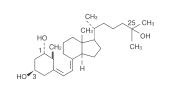
DESCRIPTION Calcitriol is a synthetic vitamin D analog which is active in the regulation of the absorption of calcium from the gastrointestinal tract and its utilization in the body. Calcitriol is available as capsules containing 0.25 mcg or 0.5 mcg calcitriol and as an oral solution containing 1 mcg/mL of calcitriol. All dosage forms contain butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) as antioxidants. The capsules contain a fractionated triglyceride of coconut oil, and the oral solution contains a fractionated triglyceride of palm seed oil. Gelatin capsule shells contain glycerin, and sorbitol, with the following dye systems: 0.25 mcg — FD&C Yellow No. 6 and titanium dioxide; 0.5 mcg — FD&C Red No. 3, FD&C Yellow No. 6 and titanium dioxide. The oral solution contains no additional adjuvants or coloring principles. Calcitriol is a white, crystalline compound which occurs naturally in humans. It has a calculated molecular weight of 416.65 and is soluble in organic solvents but relatively insoluble in water. Chemically, calcitriol is 9,10- seco(5Z,7E)-5,7,10(19)-cholestatriene-1α, 3β, 25-triol and has the following structural formula: The other names frequently used for calcitriol are 1α,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 , 1,25-DHCC, 1,25(OH) 2 D 3 and 1,25-diOHC. structure
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Capsules: 0.25 mcg calcitriol in soft gelatin, light orange, oval capsules, imprinted with R25; bottles of 30 (NDC 63304-239-30), and bottles of 100 (63304-239-01). Capsules: 0.5 mcg calcitriol in soft gelatin, dark orange, oblong capsules, imprinted with R50; bottles of 100 (NDC 63304-240-01). Oral Solution: a clear, colorless to pale yellow oral solution containing 1 mcg/mL of calcitriol; each amber glass bottle of 15 mL of oral solution supplied with 20 single-use, graduated oral dispensers (NDC 63304-241-59). Calcitriol Capsules and Oral Solution should be protected from light. Store at 59° to 86°F (15° to 30°C). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Predialysis Patients Calcitriol is indicated in the management of secondary hyperparathyroidism and resultant metabolic bone disease in patients with moderate to severe chronic renal failure (Ccr 15 to 55 mL/min) not yet on dialysis. In children, the creatinine clearance value must be corrected for a surface area of 1.73 square meters. A serum iPTH level of ≥ 100 pg/mL is strongly suggestive of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Dialysis Patients Calcitriol is indicated in the management of hypocalcemia and the resultant metabolic bone disease in patients undergoing chronic renal dialysis. In these patients, calcitriol administration enhances calcium absorption, reduces serum alkaline phosphatase levels, and may reduce elevated parathyroid hormone levels and the histological manifestations of osteitis fibrosa cystica and defective mineralization. Hypoparathyroidism Patients Calcitriol is also indicated in the management of hypocalcemia and its clinical manifestations in patients with postsurgical hypoparathyroidism, idiopathic hypoparathyroidism, and pseudohypoparathyroidism.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION The optimal daily dose of calcitriol must be carefully determined for each patient. Calcitriol can be administered orally either as a capsule (0.25 mcg or 0.50 mcg) or as an oral solution (1 mcg/mL). Calcitriol therapy should always be started at the lowest possible dose and should not be increased without careful monitoring of serum calcium. The effectiveness of calcitriol therapy is predicated on the assumption that each patient is receiving an adequate but not excessive daily intake of calcium. Patients are advised to have a dietary intake of calcium at a minimum of 600 mg daily. The U.S. RDA for calcium in adults is 800 mg to 1200 mg. To ensure that each patient receives an adequate daily intake of calcium, the physician should either prescribe a calcium supplement or instruct the patient in proper dietary measures. Because of improved calcium absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, some patients on calcitriol may be maintained on a lower calcium intake. Patients who tend to develop hypercalcemia may require only low doses of calcium or no supplementation at all. During the titration period of treatment with calcitriol, serum calcium levels should be checked at least twice weekly. When the optimal dosage of calcitriol has been determined, serum calcium levels should be checked every month (or as given below for individual indications). Samples for serum calcium estimation should be taken without a tourniquet. Dialysis Patients The recommended initial dose of calcitriol is 0.25 mcg/day. If a satisfactory response in the biochemical parameters and clinical manifestations of the disease state is not observed, dosage may be increased by 0.25 mcg/day at 4- to 8-week intervals. During this titration period, serum calcium levels should be obtained at least twice weekly, and if hypercalcemia is noted, the drug should be immediately discontinued until normocalcemia ensues (see PRECAUTIONS : General ). Phosphorus, magnesium, and alkaline phosphatase should be determined periodically. Patients with normal or only slightly reduced serum calcium levels may respond to calcitriol doses of 0.25 mcg every other day. Most patients undergoing hemodialysis respond to doses between 0.5 and 1 mcg/day. Oral calcitriol may normalize plasma-ionized calcium in some uremic patients, yet fail to suppress parathyroid hyperfunction. In these individuals with autonomous parathyroid hyperfunction, oral calcitriol may be useful to maintain normocalcemia, but has not been shown to be adequate treatment for hyperparathyroidism. Hypoparathyroidism The recommended initial dosage of calcitriol is 0.25 mcg/day given in the morning. If a satisfactory response in the biochemical parameters and clinical manifestations of the disease is not observed, the dose may be increased at 2- to 4-week intervals. During the dosage titration period, serum calcium levels should be obtained at least twice weekly and, if hypercalcemia is noted, calcitriol should be immediately discontinued until normocalcemia ensues (see PRECAUTIONS : General ). Careful consideration should also be given to lowering the dietary calcium intake. Serum calcium, phosphorus, and 24-hour urinary calcium should be determined periodically. Most adult patients and pediatric patients age 6 years and older have responded to dosages in the range of 0.5 mcg to 2 mcg daily. Pediatric patients in the 1- to 5-year age group with hypoparathyroidism have usually been given 0.25 mcg to 0.75 mcg daily. The number of treated patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism less than 6 years of age is too small to make dosage recommendations. Malabsorption is occasionally noted in patients with hypoparathyroidism; hence, larger doses of calcitriol may be needed. Predialysis Patients The recommended initial dosage of calcitriol is 0.25 mcg/day in adults and pediatric patients 3 years of age and older. This dosage may be increased if necessary to 0.5 mcg/day. For pediatric patients less than 3 years of age, the recommended initial dosage of calcitriol is 10 to 15 ng/kg/day.
