Drug Catalog - Product Detail
CHLORTHALIDONE 50MG TABS 100CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 75834-0110-01 | NIVAGEN PHARMACEUTICALS | 100 | 50MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES




Generic Name
CHLORTHALIDONE
Substance Name
CHLORTHALIDONE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA207222
Description
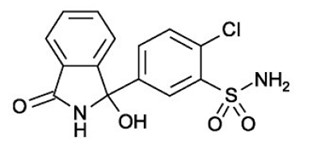
DESCRIPTION Chlorthalidone is an oral antihypertensive/diuretic. It is a monosulfamyl diuretic that differs chemically from thiazide diuretics in that a double-ring system is incorporated in its structure. It is 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-1- isoindolinyl) benzenesulfonamide with the following structural formula: chlorthalidone-strecture Molecular Formula: C 14 H 11 ClN 2 O 4 S Molecular weight: 338.776 Chlorthalidone, USP is practically insoluble in water, in ether, and in chloroform; soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in alcohol. Chlorthalidone tablets are available containing either 25 mg or 50 mg of chlorthalidone USP and the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, partially pregelatinized maize starch, sodium starch glycolate, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, ingredients of aquadry blend yellow like iron oxide yellow, lactose monohydrate, Ferrosoferric Oxide for 25 mg and ingredients of aquadry blend green like D & C Yellow #10 aluminum lake, FD & C blue #1/ Brilliant Blue FCF Aluminum Lake for 50 mg.
How Supplied
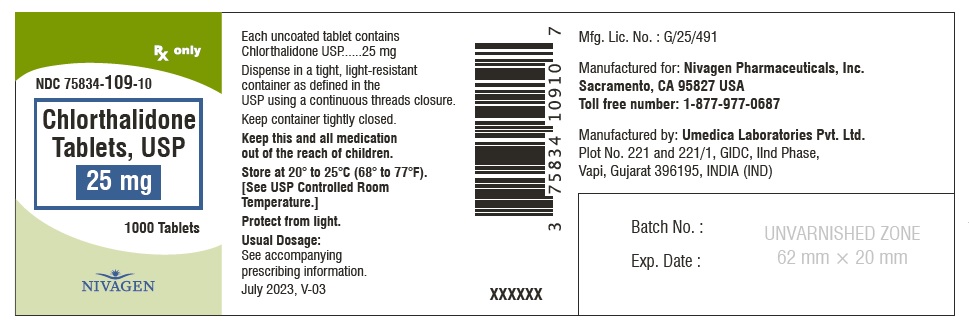
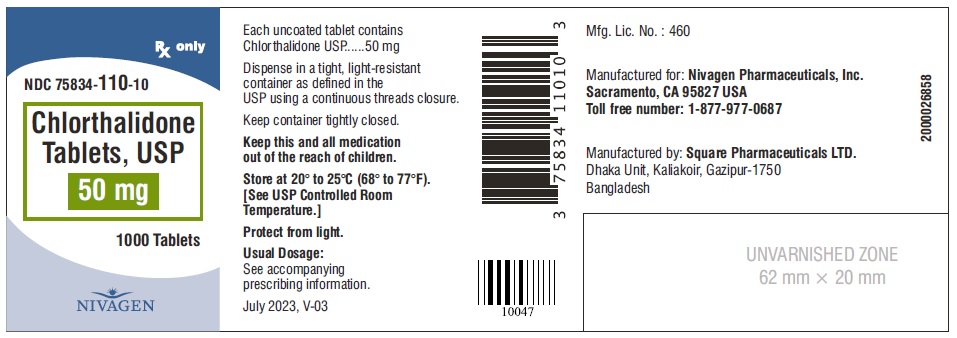
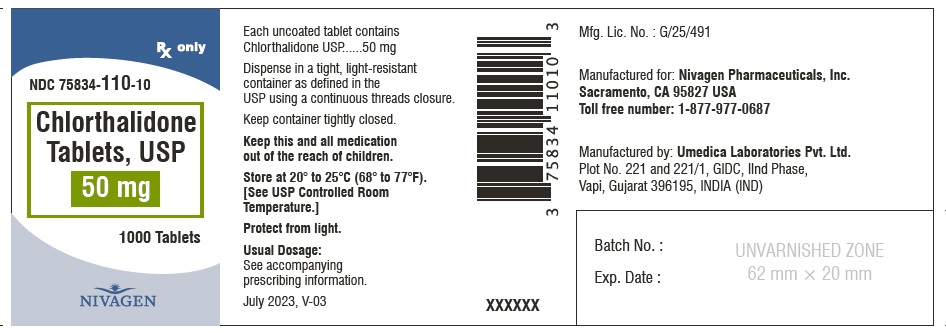
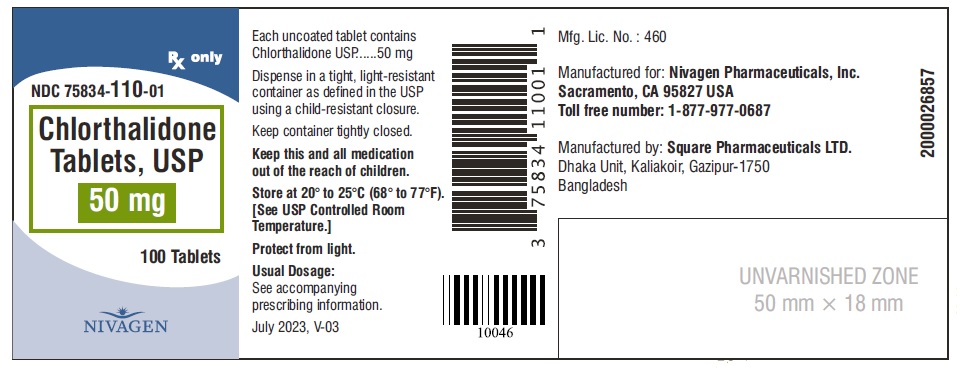
HOW SUPPLIED Chlorthalidone Tablets, USP are available containing 25 mg or 50 mg of Chlorthalidone, USP. 25 mg Tablets are Light yellow colour, round, unscored tablet, debossed with "N" on one side and plain on other side. 25 mg Tablets are supplied as follows: Bottles of 100 tablets NDC # 75834-109-01 Bottles of 1000 tablets NDC # 75834-109-10 50 mg Tablets are Light green colour, round tablet, debossed with "N" and score line on one side and plain on other side. 50 mg Tablets are supplied as follows: Bottles of 100 tablets NDC # 75834-110-01 Bottles of 1000 tablets NDC # 75834-110-10 Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP for Controlled Room Temperature.] Protect from light. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure. ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY Biochemical studies in animals have suggested reasons for the prolonged effect of chlorthalidone. Absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is slow due to its low solubility. After passage to the liver, some of the drug enters the general circulation, while some is excreted in the bile, to be reabsorbed later. In the general circulation, it is distributed widely to the tissues, but is taken up in highest concentrations by the kidneys, where amounts have been found 72 hours after ingestion, long after it has disappeared from other tissues. The drug is excreted unchanged in the urine. Manufactured for: Nivagen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Sacramento, CA 95827 USA Toll free number: 1-877-977-0687 Manufactured by: Umedica Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. Plot No.221 and 221/1, GIDC, II nd Phase, Vapi, Gujarat 396195, India (IND) Manufactured by: Square Pharmaceuticals Limited Dhaka Unit, Kaliakoir, Gazipur – 1750, Bangladesh. Revised July 2023, V-03
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Diuretics such as chlorthalidone are indicated in the management of hypertension either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs. Chlorthalidone is indicated as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy. Chlorthalidone has also been found useful in edema due to various forms of renal dysfunction, such as nephrotic syndrome, acute glomerulonephritis, and chronic renal failure. Usage in Pregnancy The routine use of diuretics in an otherwise healthy woman is inappropriate and exposes mother and fetus to unnecessary hazard. Diuretics do not prevent development of toxemia of pregnancy, and there is no satisfactory evidence that they are useful in the treatment of developed toxemia. Edema during pregnancy may arise from pathologic causes or from the physiologic and mechanical consequences of pregnancy. Chlorthalidone is indicated in pregnancy when edema is due to pathologic causes, just as it is in the absence of pregnancy (however, see PRECAUTIONS , below). Dependent edema in pregnancy, resulting from restriction of venous return by the expanded uterus, is properly treated through elevation of the lower extremities and use of support hose; use of diuretics to lower intravascular volume in this case is illogical and unnecessary. There is hypervolemia during normal pregnancy that is harmful to neither the fetus nor the mother (in the absence of cardio vascular disease), but that is associated with edema, including generalized edema, in the majority of pregnant women. If this edema produces discomfort, increased recumbency will often provide relief. In rare instances, this edema may cause extreme discomfort that is not relieved by rest. In these cases, a short course of diuretics may provide relief and be appropriate.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Therapy should be initiated with the lowest possible dose, then titrated according to individual patient response. A single dose given in the morning with food is recommended; divided daily doses are unnecessary. Hypertension Initiation Therapy, in most patients, should be initiated with a single daily dose of 15 mg. If the response is insufficient after a suitable trial, the dosage may be increased to a single daily dose of 25 mg. If additional control is required, the dosage of chlorthalidone may be increased to 30-50 mg once daily or 100 mg once daily. A second antihypertensive drug (step 2 therapy) may be added, as necessary. Dosage above 100 mg daily usually does not increase effectiveness. Increases in serum uric acid and decreases in serum potassium are dose-related over the 15 to 100 mg/day range. Maintenance Maintenance doses may be lower than initial doses and should be adjusted according to individual patient response. Effectiveness is well sustained during continued use. Edema Initiation Adults, initially 30 to 100 mg daily, or 100 mg on alternate days. Some patients may require 90 to 200 mg at these intervals or up to 200 mg daily. Dosages above this level, however, do not usually produce a greater response. Maintenance Maintenance doses may often be lower than initial doses and should be adjusted according to individual patient response. Effectiveness is well sustained during continued use.
