Drug Catalog - Product Detail
CLARITHROMYCIN ORAL SUSPENSION, USP SUSP 250MG/5ML 50ML
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00781-6023-52 | SANDOZ | 50 | 250MG/5ML | SUSPENSION |
PACKAGE FILES


Generic Name
CLARITHROMYCIN
Substance Name
CLARITHROMYCIN
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA065283
Description
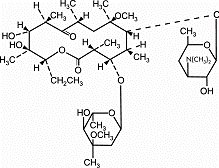
11 DESCRIPTION Clarithromycin is a semi-synthetic macrolide antimicrobial for oral use. Chemically, it is 6- 0 ‑ methylerythromycin. The molecular formula is C 38 H 69 NO 13 , and the molecular weight is 747.96. The structural formula is: Figure 1: Structure of Clarithromycin Clarithromycin is a white to off-white crystalline powder. It is soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in methanol, ethanol, and acetonitrile, and practically insoluble in water. Clarithromycin is available as granules for oral suspension. After constitution, each 5 mL of clarithromycin for oral suspension, USP contains 125 mg or 250 mg of clarithromycin. Each bottle of clarithromycin granules for oral suspension contains 1250 mg (50 mL size), 2500 mg (50 and 100 mL sizes) or 5000 mg (100 mL size) of clarithromycin and the following inactive ingredients: citric acid (anhydrous), colloidal silicon dioxide, confectioner’s sugar, fruit punch flavor, glyceryl monostearate, hypromellose, maltodextrin, methacrylic acid copolymer dispersion, poloxamer, polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80, potassium sorbate, povidone, titanium dioxide, triethyl citrate, and xanthan gum. structural formula
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Clarithromycin for oral suspension, USP is supplied in the following strengths and sizes: Total Volume After Constitution Clarithromycin Concentration After Constitution Clarithromycin Contents Per Bottle NDC 50 mL 125 mg/5 mL 1250 mg 0781-6022-52 100 mL 125 mg/5 mL 2500 mg 0781-6022-46 50 mL 250 mg/5 mL 2500 mg 0781-6023-52 100 mL 250 mg/5 mL 5000 mg 0781-6023-46 Store clarithromycin for oral suspension below 25°C (77°F) in a well-closed container [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not refrigerate clarithromycin suspension.
Indications & Usage
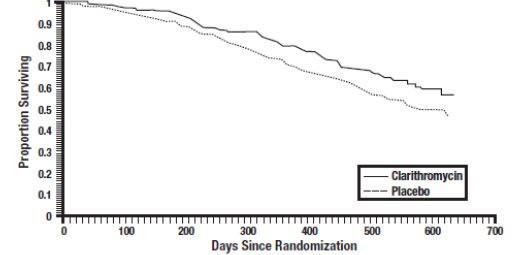
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Clarithromycin is a macrolide antimicrobial indicated for mild to moderate infections caused by designated, susceptible bacteria in the following: • Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis in Adults ( 1.1 ) • Acute Maxillary Sinusitis ( 1.2 ) • Community-Acquired Pneumonia ( 1.3 ) • Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis ( 1.4 ) • Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections ( 1.5 ) • Acute Otitis Media in Pediatric Patients ( 1.6 ) • Treatment and Prophylaxis of Disseminated Mycobacterial Infections ( 1.7 ) Limitations of Use: To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of clarithromycin and other antibacterial drugs, clarithromycin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. ( 1.9 ) 1.1 Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis Clarithromycin is indicated in adults for the treatment of mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible isolates due to Haemophilus influenzae , Haemophilus parainfluenzae , Moraxella catarrhalis , or Streptococcus pneumoniae [ see Indications and Usage ( 1.9 ) ]. 1.2 Acute Maxillary Sinusitis Clarithromycin is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible isolates due to Haemophilus influenzae , Moraxella catarrhalis , or Streptococcus pneumoniae [ see Indications and Usage (1.9) ]. 1.3 Community-Acquired Pneumonia Clarithromycin is indicated [ see Indications and Usage ( 1.9 ) ] for the treatment of mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible isolates due to: • Haemophilus influenzae (in adults) • Mycoplasma pneumoniae , Streptococcus pneumoniae , Chlamydophila pneumoniae clarithromycin [in adults and pediatric patients] 1.4 Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis Clarithromycin is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible isolates due to Streptococcus pyogenes as an alternative in individuals who cannot use first line therapy. 1.5 Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections Clarithromycin is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible isolates due to Staphylococcus aureus , or Streptococcus pyogenes . 1.6 Acute Otitis Media Clarithromycin is indicated in pediatric patients for the treatment of mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible isolates due to Haemophilus influenzae , Moraxella catarrhalis , or Streptococcus pneumoniae [ see Clinical Studies ( 14.2 ) ]. 1.7 Treatment and Prophylaxis of Disseminated Mycobacterial Infections Clarithromycin is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible isolates due to Mycobacterium avium or Mycobacterium intracellulare in patients with advanced HIV infection [ see Clinical Studies ( 14.1 ) ]. 1.9 Limitations of Use There is resistance to macrolides in certain bacterial infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus . Susceptibility testing should be performed when clinically indicated. 1.10 Usage To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of clarithromycin and other antibacterial drugs, clarithromycin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Pediatric Patients: Clarithromycin 15 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hours for 10 days ( 2.4 ) • Mycobacterial Infections: Clarithromycin 500 mg every 12 hours; Clarithromycin 7.5 mg/kg up to 500 mg every 12 hours in pediatric patients ( 2.5 ) • Reduce dose in moderate renal impairment with concomitant atazanavir or ritonavir-containing regimens and in severe renal impairment ( 2.6 ) 2.1 Important Administration Instructions Clarithromycin for oral suspension may be given with or without food. 2.4 Pediatric Dosage The recommended daily dosage is 15 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hours for 10 days (up to the adult dose). Refer to dosage regimens for mycobacterial infections in pediatric patients for additional dosage information [ see Dosage and Administration ( 2.5 ) ]. 2.5 Dosage Regimens for Mycobacterial Infections For the treatment of disseminated infection due to Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC), clarithromycin is recommended as the primary agents. Clarithromycin should be used in combination with other antimycobacterial drugs (e.g. ethambutol) that have shown in vitro activity against MAC or clinical benefit in MAC treatment [ see Clinical Studies ( 14.1 ) ]. Adult Patients For treatment and prophylaxis of mycobacterial infections in adults, the recommended dose of clarithromycin is 500 mg every 12 hours. Pediatric Patients For treatment and prophylaxis of mycobacterial infections in pediatric patients, the recommended dose is 7.5 mg/kg every 12 hours up to 500 mg every 12 hours. [ see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4 ) and Clinical Studies ( 14.1 ) ]. Clarithromycin therapy should continue if clinical response is observed. Clarithromycin can be discontinued when the patient is considered at low risk of disseminated infection. 2.6 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment See Table 2 for dosage adjustment in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment with or without concomitant atazanavir or ritonavir-containing regimens [ see Drug Interactions ( 7) ]. Table 2. Clarithromycin Dosage Adjustments in Patients with Renal Impairment Recommended ClarithromycinDosage Reduction Patients with severe renal impairment (CL cr of <30 mL/min) Reduce the dosage of Clarithromycin by 50% Patients with moderate renal impairment (CL cr of 30 to 60 mL/min) taking concomitant atazanavir or ritonavir-containing regimens Reduce the dosage of Clarithromycin by 50% Patients with severe renal impairment (CL cr of <30 mL/min) taking concomitant atazanavir or ritonavir-containing regimens Reduce the dosage of Clarithromycin by 75% 2.7 Dosage Adjustment Due to Drug Interactions Decrease the dose of clarithromycin by 50 % when co-administered with atazanavir [ see Drug Interactions ( 7 ) ]. Dosage adjustments for other drugs when co-administered with clarithromycin may be recommended due to drug interactions [ see Drug Interactions ( 7 ) ]. 2.8 Reconstitution of Clarithromycin for Oral Suspension The supplied clarithromycin granules must be reconstituted with water prior to administration of clarithromycin for oral suspension. Table 3 below indicates the volume of water to be added when reconstituting. To reconstitute: a. Add half the volume of water to the bottle containing the clarithromycin granules and shake vigorously. b. Add the remainder of water to the bottle and shake. Shake well before each use. After mixing, store at 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) and use within 14 days. Do not refrigerate. Table 3. Volume of Water to be Added When Reconstituting Clarithromycin Granules Total Volume After Reconstitution Clarithromycin Concentration After Reconstitution Amount of Water to be Added 50 mL 125 mg/5 mL 29.5 mL 100 mL 125 mg/5 mL 59 mL 50 mL 250 mg/5 mL 28.5 mL 100 mL 250 mg/5 mL 57 mL
