Drug Catalog - Product Detail
DESVENLAFAXINE SUCCINATE TAB ER 24HR 100MG 90CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51991-0312-90 | BRECKENRIDGE | 90 | 100MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES



Generic Name
DESVENLAFAXINE SUCCINATE
Substance Name
DESVENLAFAXINE SUCCINATE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA204003
Description
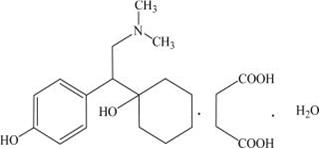
11 DESCRIPTION Desvenlafaxine is an extended-release tablet for oral administration that contains desvenlafaxine succinate, USP, a structurally novel SNRI for the treatment of MDD. Desvenlafaxine (O-desmethylvenlafaxine) is the major active metabolite of the antidepressant venlafaxine, a medication used to treat major depressive disorder. Desvenlafaxine is designated RS -4-[2-dimethylamino-1-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)ethyl]phenol and has the empirical formula of C 16 H 25 NO 2 (free base) and C 16 H 25 NO 2 •C 4 H 6 O 4 •H 2 O (succinate monohydrate). Desvenlafaxine succinate monohydrate has a molecular weight of 399.48. The structural formula is shown below. Desvenlafaxine succinate, USP is a white to off-white powder that is soluble in water. The solubility of desvenlafaxine succinate is pH dependent. Its octanol:aqueous system (at pH 7) partition coefficient is 0.21. Desvenlafaxine is formulated as an extended-release tablet for once-a-day oral administration. Each tablet contains 38 mg, 76 mg or 152 mg of desvenlafaxine succinate equivalent to 25 mg, 50 mg or 100 mg of desvenlafaxine, respectively. Inactive ingredients for the 25 mg tablet consist of hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, talc and film coating, which consists of hypromellose, iron oxide yellow, iron oxide red, iron oxide black, polyethylene glycol, talc, and titanium dioxide. Inactive ingredients for the 50 mg tablet consist of hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, talc and film coating, which consists of hypromellose, iron oxide red, polyethylene glycol, talc, and titanium dioxide. Inactive ingredients for the 100 mg tablet consist of hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, talc and film coating, which consists of hypromellose, iron oxide black, iron oxide red, polyethylene glycol, talc, and titanium dioxide. Structure
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Desvenlafaxine Extended-Release Tablets are available as follows: 25 mg, tan colored, round, biconvex tablets, debossed with ‘L634’ on one side and plain on other side. NDC 51991-006-33, bottle of 30 tablets in unit-of-use package NDC 51991-006-90, bottle of 90 tablets in unit-of-use package NDC 51991-006-01, bottle of 100 tablets NDC 51991-006-10, bottle of 1,000 tablets NDC 51991-006-11, carton of 100 (10 x 10) unit-dose tablets NDC 51991-006-80, carton of 80 (10 x 8) unit-dose tablets 50 mg, light pink colored, round, biconvex tablets, debossed with ‘L349’ on one side and plain on other side. NDC 51991-311-14, bottle of 14 tablets in unit-of-use package NDC 51991-311-33, bottle of 30 tablets in unit-of-use package NDC 51991-311-90, bottle of 90 tablets in unit-of-use package NDC 51991-311-01, bottle of 100 tablets NDC 51991-311-10, bottle of 1,000 tablets NDC 51991-311-11, carton of 100 (10 x 10) unit-dose tablets NDC 51991-311-80, carton of 80 (10 x 8) unit-dose tablets 100 mg, dark brown to red colored, round, biconvex tablets, debossed with ‘L350’ on one side and plain on other side. NDC 51991-312-14, bottle of 14 tablets in unit-of-use package NDC 51991-312-33, bottle of 30 tablets in unit-of-use package NDC 51991-312-90, bottle of 90 tablets in unit-of-use package NDC 51991-312-01, bottle of 100 tablets NDC 51991-312-10, bottle of 1,000 tablets NDC 51991-312-11, carton of 100 (10 x 10) unit-dose tablets NDC 51991-312-80, carton of 80 (10 x 8) unit-dose tablets Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature] Each tablet contains 38 mg, 76 mg or 152 mg of desvenlafaxine succinate equivalent to 25 mg, 50 mg or 100 mg of desvenlafaxine, respectively.
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Desvenlafaxine is indicated for the treatment of adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) [see Clinical Studies (14)] . Desvenlafaxine is a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) indicated for the treatment of adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) ( 1 ).
Dosage and Administration
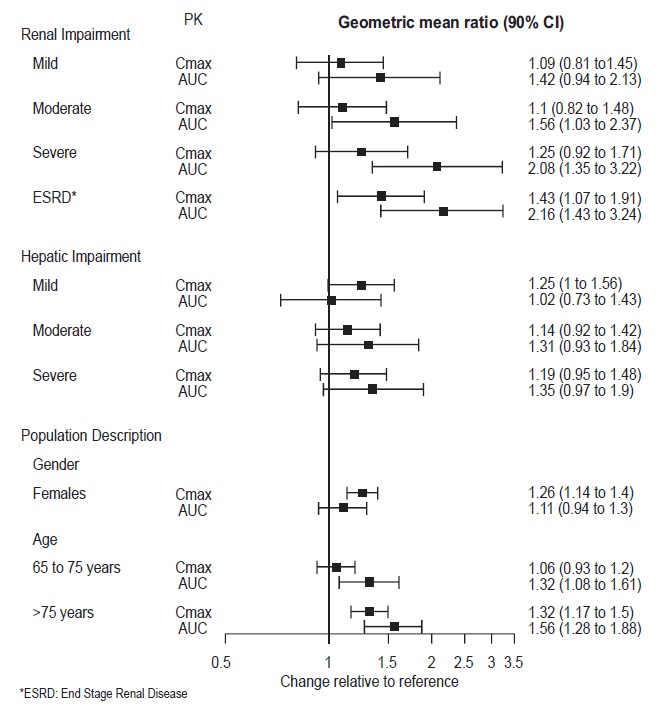
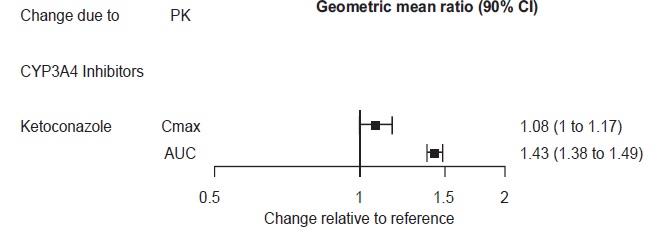
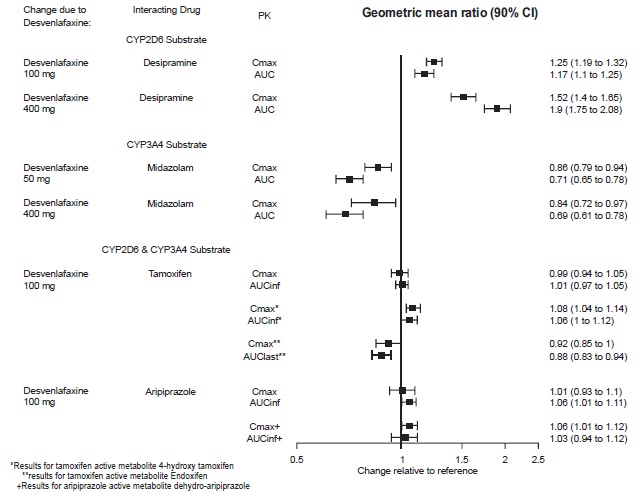
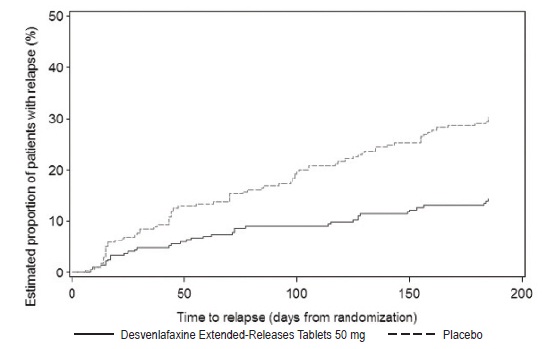
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION •Recommended dose: 50 mg once daily with or without food ( 2.1 ). •There was no evidence that doses greater than 50 mg per day confer any additional benefit ( 2.1 ). •The 25 mg per day dose is intended for a gradual reduction in dose when discontinuing treatment or dosing in severe renal and end-stage renal disease patients ( 2.1 ). •Discontinuation: Reduce dose gradually whenever possible ( 2.1 ). •Take tablets whole; do not divide, crush, chew, or dissolve ( 2.1 ). •Moderate renal impairment: Maximum dose 50 mg per day ( 2.2 ). •Severe renal impairment and end-stage renal disease: Maximum dose 25 mg per day or 50 mg every other day ( 2.2 ). •Moderate to severe hepatic impairment: Maximum dose 100 mg per day ( 2.3 ). 2.1 General Instructions for Use The recommended dose for desvenlafaxine is 50 mg once daily, with or without food. The 50 mg dose is both a starting dose and the therapeutic dose. Desvenlafaxine should be taken at approximately the same time each day. Tablets must be swallowed whole with fluid and not divided, crushed, chewed, or dissolved. In clinical studies, doses of 10 mg to 400 mg per day were studied. In clinical studies, doses of 50 mg to 400 mg per day were shown to be effective, although no additional benefit was demonstrated at doses greater than 50 mg per day and adverse reactions and discontinuations were more frequent at higher doses. The 25 mg per day dose is intended for a gradual reduction in dose when discontinuing treatment. When discontinuing therapy, gradual dose reduction is recommended whenever possible to minimize discontinuation symptoms [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] . 2.2 Dosage Recommendations for Patients with Renal Impairment The maximum recommended dose in patients with moderate renal impairment (24-hr creatinine clearance [CL Cr ] = 30 to 50 mL/min, Cockcroft-Gault [C-G]) is 50 mg per day. The maximum recommended dose in patients with severe renal impairment (CL Cr 15 to 29 mL/min, C-G) or end-stage renal disease (ESRD, CL Cr < 15 mL/min, C-G) is 25 mg every day or 50 mg every other day. Supplemental doses should not be given to patients after dialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. 2.3 Dosage Recommendations for Patients with Hepatic Impairment The recommended dose in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 7 to 15) is 50 mg per day. Dose escalation above 100 mg per day is not recommended [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. 2.4 Maintenance/Continuation/Extended Treatment It is generally agreed that acute episodes of major depressive disorder require several months or longer of sustained pharmacologic therapy. Longer-term efficacy of desvenlafaxine (50 to 400 mg) was established in two maintenance trials [see Clinical Studies (14)] . Patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the need for continued treatment. 2.5 Discontinuing Desvenlafaxine Adverse reactions may occur upon discontinuation of desvenlafaxine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. Gradually reduce the dosage rather than stopping desvenlafaxine abruptly when discontinuing therapy with desvenlafaxine. In some patients, discontinuation may need to occur over a period of several months. 2.6 Switching Patients From Other Antidepressants to Desvenlafaxine Discontinuation symptoms have been reported when switching patients from other antidepressants, including venlafaxine, to desvenlafaxine. Tapering of the initial antidepressant may be necessary to minimize discontinuation symptoms. 2.7 Switching Patients to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) Intended to Treat Psychiatric Disorders At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders and initiation of therapy with desvenlafaxine. Conversely, at least 7 days should be allowed after stopping desvenlafaxine before starting an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders [see Contraindications (4)] . 2.8 Use of Desvenlafaxine with other MAOIs such as Linezolid or Methylene Blue Do not start desvenlafaxine in a patient who is being treated with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue because there is increased risk of serotonin syndrome. In a patient who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition, other interventions, including hospitalization, should be considered [see Contraindications (4)] . In some cases, a patient already receiving desvenlafaxine therapy may require urgent treatment with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. If acceptable alternatives to linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are not available and the potential benefits of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are judged to outweigh the risks of serotonin syndrome in a particular patient, desvenlafaxine should be stopped promptly, and linezolid or intravenous methylene blue can be administered. The patient should be monitored for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for 7 days or until 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, whichever comes first. Therapy with desvenlafaxine may be resumed 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] . The risk of administering methylene blue by non-intravenous routes (such as oral tablets or by local injection) or in intravenous doses much lower than 1 mg/kg with desvenlafaxine is unclear. The clinician should, nevertheless, be aware of the possibility of emergent symptoms of serotonin syndrome with such use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
