Drug Catalog - Product Detail
DIVALPROEX SODIUM DR TB 500MG 500
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62756-0798-13 | SUN PHARMACEUTICALS | 500 | 500MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES

Generic Name
DIVALPROEX SODIUM
Substance Name
DIVALPROEX SODIUM
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA078597
Description
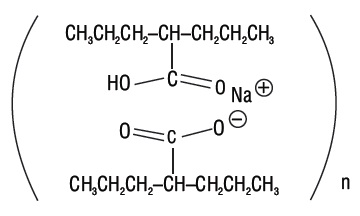
11 DESCRIPTION Divalproex sodium is a stable coordination compound comprised of sodium valproate and valproic acid in a 1:1 molar relationship. Chemically it is designated as sodium hydrogen bis(2-propylpentanoate). Divalproex sodium has the following structure: Divalproex sodium occurs as a white powder with a characteristic odor. Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are for oral administration. Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets, USP are supplied in three dosage strengths containing divalproex sodium USP equivalent to 125 mg, 250 mg, or 500 mg of valproic acid. Inactive Ingredients Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, povidone, pregelatinized maize starch, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, triacetin, methacrylic acid copolymer type C, talc, triethyl citrate, colloidal anhydrous silica, sodium bicarbonate, and sodium lauryl sulfate. Imprinting ink contains shellac glaze, iron oxide black, N-butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and ammonium hydroxide. In addition, individual tablets contain: 125 mg tablets: FD&C Red #40, and FD&C Blue #2 250 mg tablets: FD&C Yellow #6, and iron oxide yellow 500 mg tablets: D&C Red #30, FD&C Blue #2, and iron oxide red spl-divalproex-structure
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING The 250 mg tablets are orange colored, oval shaped, biconvex coated tablets imprinted ‘797’ with black ink on one side and plain on the other side. Bottles of 60 NDC 68071-3553-6 The 500 mg tablets are pink colored, oval shaped, biconvex coated tablets imprinted ‘798’ with black ink on one side and plain on the other side. Bottles of 30 with Child Resistant Cap, NDC 62756-798-83 Bottles of 100 with Child Resistant Cap, NDC 62756-798-88 Bottles of 100, NDC 62756-798-08 Bottles of 500, NDC 62756-798-13 Bottles of 1,000, NDC 62756-798-18 Recommended Storage: Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30° C (59° to 86° F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Indications & Usage
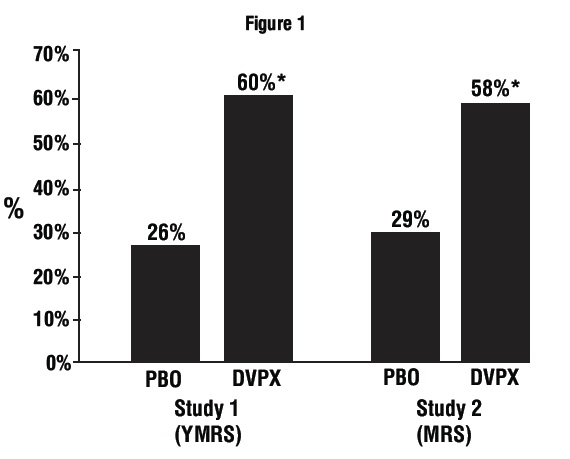
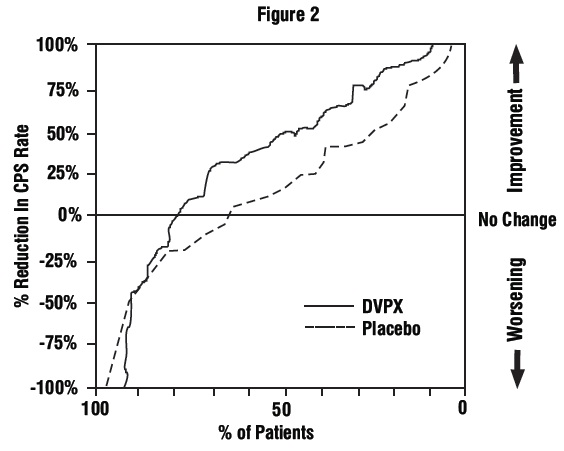
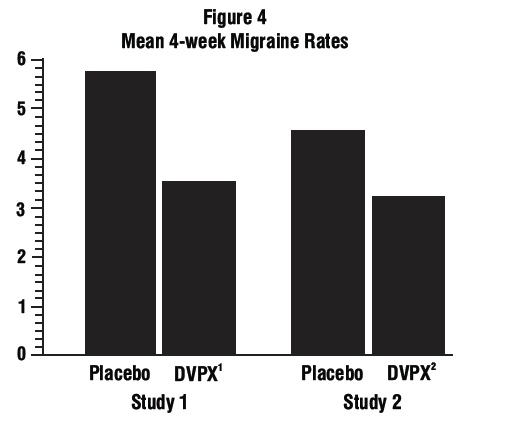
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Divalproex sodium is an anti-epileptic drug indicated for: Treatment of manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder ( 1.1 ) Monotherapy and adjunctive therapy of complex partial seizures and simple and complex absence seizures; adjunctive therapy in patients with multiple seizure types that include absence seizures ( 1.2 ) Prophylaxis of migraine headaches ( 1.3 ) 1.1 Mania Divalproex sodium is a valproate and is indicated for the treatment of the manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder. A manic episode is a distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood. Typical symptoms of mania include pressure of speech, motor hyperactivity, reduced need for sleep, flight of ideas, grandiosity, poor judgment, aggressiveness, and possible hostility. The efficacy of divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets was established in 3-week trials with patients meeting DSM-III-R criteria for bipolar disorder who were hospitalized for acute mania [see Clinical Studies ( 14.1 )] . The safety and effectiveness of divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets for long-term use in mania, i.e., more than 3 weeks, has not been demonstrated in controlled clinical trials. Therefore, healthcare providers who elect to use divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets for extended periods should continually reevaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient. 1.2 Epilepsy Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are indicated as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of patients with complex partial seizures that occur either in isolation or in association with other types of seizures. Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are also indicated for use as sole and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of simple and complex absence seizures, and adjunctively in patients with multiple seizure types that include absence seizures. Simple absence is defined as very brief clouding of the sensorium or loss of consciousness accompanied by certain generalized epileptic discharges without other detectable clinical signs. Complex absence is the term used when other signs are also present. 1.3 Migraine Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are indicated for prophylaxis of migraine headaches. There is no evidence that divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are useful in the acute treatment of migraine headaches. 1.4 Important Limitations Because of the risk to the fetus of decreased IQ, neurodevelopmental disorders, neural tube defects, and other major congenital malformations, which may occur very early in pregnancy, valproate should not be used to treat women with epilepsy or bipolar disorder who are pregnant or who plan to become pregnant unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable. Valproate should not be administered to a woman of childbearing potential unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.1), and Patient Counseling Information (17)]. For prophylaxis of migraine headaches, divalproex sodium is contraindicated in women who are pregnant and in women of childbearing potential who are not using effective contraception [see Contraindications (4)].
Dosage and Administration
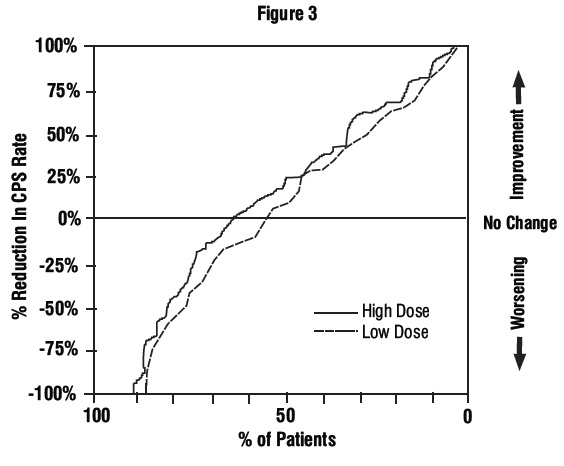
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are intended for oral administration. Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets should be swallowed whole and should not be crushed or chewed. Patients should be informed to take divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets every day as prescribed. If a dose is missed it should be taken as soon as possible, unless it is almost time for the next dose. If a dose is skipped, the patient should not double the next dose. Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are administered orally in divided doses. Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets should be swallowed whole and should not be crushed or chewed ( 2.1 , 2.2 ). Mania: Initial dose is 750 mg daily, increasing as rapidly as possible to achieve therapeutic response or desired plasma level ( 2.1 ). The maximum recommended dosage is 60 mg/kg/day ( 2.1 , 2.2 ). Complex Partial Seizures: Start at 10 to 15 mg/kg/day, increasing at 1 week intervals by 5 to 10 mg/kg/day to achieve optimal clinical response; if response is not satisfactory, check valproate plasma level; see full prescribing information for conversion to monotherapy ( 2.2 ). The maximum recommended dosage is 60 mg/kg/day ( 2.1 , 2.2 ). Absence Seizures: Start at 15 mg/kg/day, increasing at 1 week intervals by 5 to 10 mg/kg/day until seizure control or limiting side effects ( 2.2 ). The maximum recommended dosage is 60 mg/kg/day ( 2.1 , 2.2 ). Migraine: The recommended starting dose is 250 mg twice daily, thereafter increasing to a maximum of 1,000 mg/day as needed ( 2.3 ). 2.1 Mania Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are administered orally. The recommended initial dose is 750 mg daily in divided doses. The dose should be increased as rapidly as possible to achieve the lowest therapeutic dose which produces the desired clinical effect or the desired range of plasma concentrations. In placebo-controlled clinical trials of acute mania, patients were dosed to a clinical response with a trough plasma concentration between 50 and 125 mcg/mL. Maximum concentrations were generally achieved within 14 days. The maximum recommended dosage is 60 mg/kg/day. There is no body of evidence available from controlled trials to guide a clinician in the longer term management of a patient who improves during divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets treatment of an acute manic episode. While it is generally agreed that pharmacological treatment beyond an acute response in mania is desirable, both for maintenance of the initial response and for prevention of new manic episodes, there are no data to support the benefits of divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets in such longer-term treatment. Although there are no efficacy data that specifically address longer-term antimanic treatment with divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets, the safety of divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets in long-term use is supported by data from record reviews involving approximately 360 patients treated with divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets for greater than 3 months. 2.2 Epilepsy Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are administered orally. Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are indicated as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in complex partial seizures in adults and pediatric patients down to the age of 10 years, and in simple and complex absence seizures. As the divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets dosage is titrated upward, concentrations of clonazepam, diazepam, ethosuximide, lamotrigine, tolbutamide, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and/or phenytoin may be affected [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] . Complex Partial Seizures For adults and children 10 years of age or older. Monotherapy (Initial Therapy) Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets have not been systematically studied as initial therapy. Patients should initiate therapy at 10 to 15 mg/kg/day. The dosage should be increased by 5 to 10 mg/kg/week to achieve optimal clinical response. Ordinarily, optimal clinical response is achieved at daily doses below 60 mg/kg/day. If satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved, plasma levels should be measured to determine whether or not they are in the usually accepted therapeutic range (50 to 100 mcg/mL). No recommendation regarding the safety of valproate for use at doses above 60 mg/kg/day can be made. The probability of thrombocytopenia increases significantly at total trough valproate plasma concentrations above 110 mcg/mL in females and 135 mcg/mL in males. The benefit of improved seizure control with higher doses should be weighed against the possibility of a greater incidence of adverse reactions. Conversion to Monotherapy Patients should initiate therapy at 10 to 15 mg/kg/day. The dosage should be increased by 5 to 10 mg/kg/week to achieve optimal clinical response. Ordinarily, optimal clinical response is achieved at daily doses below 60 mg/kg/day. If satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved, plasma levels should be measured to determine whether or not they are in the usually accepted therapeutic range (50 to 100 mcg/mL). No recommendation regarding the safety of valproate for use at doses above 60 mg/kg/day can be made. Concomitant antiepilepsy drug (AED) dosage can ordinarily be reduced by approximately 25% every 2 weeks. This reduction may be started at initiation of divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets therapy, or delayed by 1 to 2 weeks if there is a concern that seizures are likely to occur with a reduction. The speed and duration of withdrawal of the concomitant AED can be highly variable, and patients should be monitored closely during this period for increased seizure frequency. Adjunctive Therapy Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets may be added to the patient's regimen at a dosage of 10 to 15 mg/kg/day. The dosage may be increased by 5 to 10 mg/kg/week to achieve optimal clinical response. Ordinarily, optimal clinical response is achieved at daily doses below 60 mg/kg/day. If satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved, plasma levels should be measured to determine whether or not they are in the usually accepted therapeutic range (50 to 100 mcg/mL). No recommendation regarding the safety of valproate for use at doses above 60 mg/kg/day can be made. If the total daily dose exceeds 250 mg, it should be given in divided doses. In a study of adjunctive therapy for complex partial seizures in which patients were receiving either carbamazepine or phenytoin in addition to valproate, no adjustment of carbamazepine or phenytoin dosage was needed [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] . However, since valproate may interact with these or other concurrently administered AEDs as well as other drugs, periodic plasma concentration determinations of concomitant AEDs are recommended during the early course of therapy [see Drug Interactions (7)] . Simple and Complex Absence Seizures The recommended initial dose is 15 mg/kg/day, increasing at one week intervals by 5 to 10 mg/kg/day until seizures are controlled or side effects preclude further increases. The maximum recommended dosage is 60 mg/kg/day. If the total daily dose exceeds 250 mg, it should be given in divided doses. A good correlation has not been established between daily dose, serum concentrations, and therapeutic effect. However, therapeutic valproate serum concentrations for most patients with absence seizures is considered to range from 50 to 100 mcg/mL. Some patients may be controlled with lower or higher serum concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . As the divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets dosage is titrated upward, blood concentrations of phenobarbital and/or phenytoin may be affected [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] . Antiepilepsy drugs should not be abruptly discontinued in patients in whom the drug is administered to prevent major seizures because of the strong possibility of precipitating status epilepticus with attendant hypoxia and threat to life. In epileptic patients previously receiving valproic acid therapy, divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets should be initiated at the same daily dose and dosing schedule. After the patient is stabilized on divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets, a dosing schedule of two or three times a day may be elected in selected patients. 2.3 Migraine Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are indicated for prophylaxis of migraine headaches in adults. Divalproex sodium delayed-release tablets are administered orally. The recommended starting dose is 250 mg twice daily. Some patients may benefit from doses up to 1,000 mg/day. In the clinical trials, there was no evidence that higher doses led to greater efficacy. 2.4 General Dosing Advice Dosing in Elderly Patients Due to a decrease in unbound clearance of valproate and possibly a greater sensitivity to somnolence in the elderly, the starting dose should be reduced in these patients. Dosage should be increased more slowly and with regular monitoring for fluid and nutritional intake, dehydration, somnolence, and other adverse reactions. Dose reductions or discontinuation of valproate should be considered in patients with decreased food or fluid intake and in patients with excessive somnolence. The ultimate therapeutic dose should be achieved on the basis of both tolerability and clinical response [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14), Use in Specific Populations (8.5), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Dose-Related Adverse Reactions The frequency of adverse effects (particularly elevated liver enzymes and thrombocytopenia) may be dose-related. The probability of thrombocytopenia appears to increase significantly at total valproate concentrations of ≥ 110 mcg/mL (females) or ≥ 135 mcg/mL (males) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)] . The benefit of improved therapeutic effect with higher doses should be weighed against the possibility of a greater incidence of adverse reactions. G.I. Irritation Patients who experience G.I. irritation may benefit from administration of the drug with food or by slowly building up the dose from an initial low level. 2.5 Dosing in Patients Taking Rufinamide Patients stabilized on rufinamide before being prescribed valproate should begin valproate therapy at a low dose, and titrate to a clinically effective dose [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
