Drug Catalog - Product Detail
FOSINOPRIL SODIUM 40MG TB 90
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43547-0388-09 | SOLCO HEALTHCARE | 90 | 40MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES



Generic Name
FOSINOPIRL SODIUM
Substance Name
FOSINOPRIL SODIUM
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA205670
Description
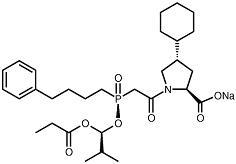
DESCRIPTION Fosinopril sodium is the sodium salt of fosinopril, the ester prodrug of an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, fosinoprilat. It contains a phosphinate group capable of specific binding to the active site of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Fosinopril sodium is designated chemically as: L-proline, 4-cyclohexyl-1-[[[2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy) propoxy] (4-phenylbutyl) phosphinyl] acetyl]-, sodium salt, trans- . Fosinopril sodium is a white to off-white crystalline powder. It is soluble in water (100 mg/mL), methanol, and ethanol and slightly soluble in hexane. Its structural formula is: C 30 H 45 NNaO 7 P M.W. 585.65 Fosinopril sodium, USP, is available for oral administration as 10 mg, 20 mg, and 40 mg tablets. Inactive ingredients include: crospovidone, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, and sodium stearyl fumarate. D:\FOSINOPRIL SODIUM\FOSINOPRILSODIUM-TEVA,2009\SPL-FOSINOPRILSODIUM07232012-TEVA,2009\6213b69f-39e1-4f48-a110-a83bd5459c4a-01.jpg
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Fosinopril sodium tablets USP, 10 mg: White to off-white, capsule-shaped tablets, both sides scored, debossed with “S|10” on one side and “|” on the other side. They are supplied in bottles of 90 (NDC 43547-386-09) and 1000 (NDC 43547-386-11). Fosinopril sodium tablets USP, 20 mg: White to off-white, round tablets debossed with “S 20” on one side and plain on the other side. They are supplied in bottles of 90 (NDC 43547-387-09) and 1000 (NDC 43547-387-11). Fosinopril sodium tablets USP, 40 mg: White to off-white, round tablets debossed with “S 40” on one side and plain on the other side. They are supplied in bottles of 90 (NDC 43547-388-09) and 1000 (NDC 43547-388-11).
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Fosinopril sodium tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension. They may be used alone or in combination with thiazide diuretics. Fosinopril sodium tablets are indicated in the management of heart failure as adjunctive therapy when added to conventional therapy including diuretics with or without digitalis (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ). In using fosinopril sodium, consideration should be given to the fact that another angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, captopril, has caused agranulocytosis, particularly in patients with renal impairment or collagen-vascular disease. Available data are insufficient to show that fosinopril sodium does not have a similar risk (see WARNINGS ). In considering use of fosinopril sodium, it should be noted that in controlled trials ACE inhibitors have an effect on blood pressure that is less in black patients than in non-blacks. In addition, ACE inhibitors (for which adequate data are available) cause a higher rate of angioedema in black than in non-black patients (see WARNINGS , Head and Neck Angioedema and Intestinal Angioedema ).
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Hypertension Adults The recommended initial dose of fosinopril sodium tablets USP is 10 mg once a day, both as monotherapy and when the drug is added to a diuretic. Dosage should then be adjusted according to blood pressure response at peak (2 to 6 hours) and trough (about 24 hours after dosing) blood levels. The usual dosage range needed to maintain a response at trough is 20 to 40 mg but some patients appear to have a further response to 80 mg. In some patients treated with once daily dosing, the antihypertensive effect may diminish toward the end of the dosing interval. If trough response is inadequate, dividing the daily dose should be considered. If blood pressure is not adequately controlled with fosinopril sodium tablets USP alone, a diuretic may be added. Concomitant administration of fosinopril sodium tablets USP with potassium supplements, potassium salt substitutes, or potassium-sparing diuretics can lead to increases of serum potassium (see PRECAUTIONS ). In patients who are currently being treated with a diuretic, symptomatic hypotension occasionally can occur following the initial dose of fosinopril sodium tablets USP. To reduce the likelihood of hypotension, the diuretic should, if possible, be discontinued 2 to 3 days prior to beginning therapy with fosinopril sodium tablets USP (see WARNINGS ). Then, if blood pressure is not controlled with fosinopril sodium tablets USP alone, diuretic therapy should be resumed. If diuretic therapy cannot be discontinued, an initial dose of 10 mg of fosinopril sodium tablets USP should be used with careful medical supervision for several hours and until blood pressure has stabilized (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS , Information for Patients and Drug Interactions ). Since concomitant administration of fosinopril sodium tablets USP with potassium supplements, or potassium-containing salt substitutes or potassium-sparing diuretics may lead to increases in serum potassium, they should be used with caution (see PRECAUTIONS ). Pediatrics In children, doses of fosinopril sodium tablets between 0.1 and 0.6 mg/kg have been studied and shown to reduce blood pressure to a similar extent (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY , Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects ). Based on this, the recommended dose of fosinopril sodium tablets USP in children weighing more than 50 kg is 5 to 10 mg once per day as monotherapy. An appropriate dosage strength is not available for children weighing less than 50 kg. Heart Failure Digitalis is not required for fosinopril sodium tablets USP to manifest improvements in exercise tolerance and symptoms. Most placebo-controlled clinical trial experience has been with both digitalis and diuretics present as background therapy. The usual starting dose of fosinopril sodium tablets USP should be 10 mg once daily. Following the initial dose of fosinopril sodium tablets USP, the patient should be observed under medical supervision for at least 2 hours for the presence of hypotension or orthostasis, and if present, until blood pressure stabilizes. An initial dose of 5 mg is preferred in heart failure patients with moderate to severe renal failure or those who have been vigorously diuresed. Dosage should be increased, over a several week period, to a dose that is maximal and tolerated but not exceeding 40 mg once daily. The usual effective dosage range is 20 to 40 mg once daily. The appearance of hypotension, orthostasis, or azotemia early in dose titration should not preclude further careful dose titration. Consideration should be given to reducing the dose of concomitant diuretic. For Hypertensive or Heart Failure Patients With Renal Impairment In patients with impaired renal function, the total body clearance of fosinoprilat is approximately 50% slower than in patients with normal renal function. Since hepatobiliary elimination partially compensates for diminished renal elimination, the total body clearance of fosinoprilat does not differ appreciably with any degree of renal insufficiency (creatinine clearances < 80 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), including end-stage renal failure (creatinine clearance < 10 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ). This relative constancy of body clearance of active fosinoprilat, resulting from the dual route of elimination, permits use of the usual dose in patients with any degree of renal impairment (see WARNINGS , Anaphylactoid Reactions During Membrane Exposure and PRECAUTIONS , Hemodialysis ).
