Drug Catalog - Product Detail
GABAPENTIN 100MG CAP 1000CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70010-0108-10 | GRANULES PHARMACEUTICALS | 1000 | MG | CAPSULE |
PACKAGE FILES





Generic Name
GABAPENTIN
Substance Name
GABAPENTIN
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA075360
Description
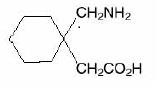
11 DESCRIPTION Gabapentin is described as 1-(aminomethyl) cyclohexaneacetic acid with a molecular formula of C 9 H 17 NO 2 and a molecular weight of 171.24. Gabapentin is a white to off-white crystalline solid with a pK a1 of 3.7 and a pK a2 of 10.7. It is freely soluble in water and both basic and acidic aqueous solutions. The log of the partition coefficient (n-octanol/0.05M phosphate buffer) at pH 7.4 is -1.25. It has the following structural formula: Gabapentin capsules, USP are for oral administration and contain 100 mg, 300 mg and 400 mg of gabapentin. In addition, each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium and magnesium stearate. The 100 mg, 300 mg and 400 mg capsule imprinting ink contains the following inactive ingredients: black iron oxide E172; butyl alcohol; dehydrated alcohol; isopropyl alcohol; potassium hydroxide; propylene glycol; purified water; shellac E904 and strong ammonia solution. The 100 mg capsule shell contains gelatin and titanium dioxide. The 300 mg capsule shell contains gelatin, titanium dioxide and yellow iron oxide. The 400 mg capsule shell contains gelatin, red iron oxide, titanium oxide and yellow iron oxide. gaba-structure.jpg
How Supplied
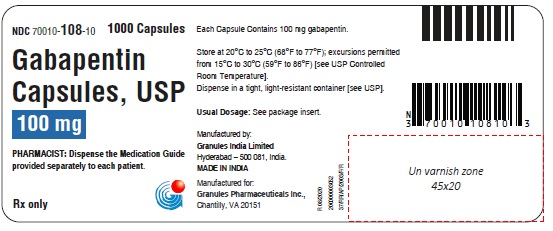
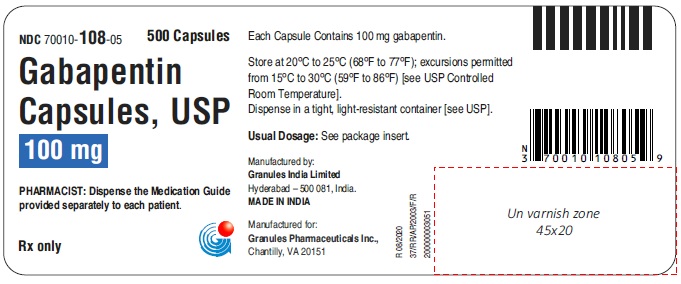
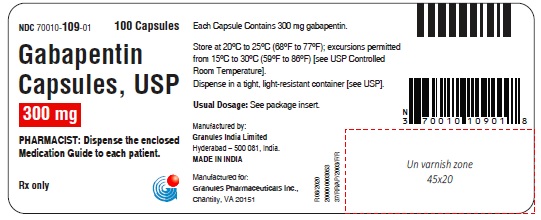
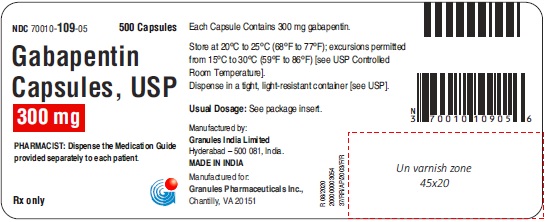
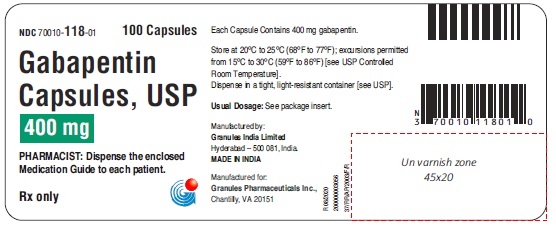
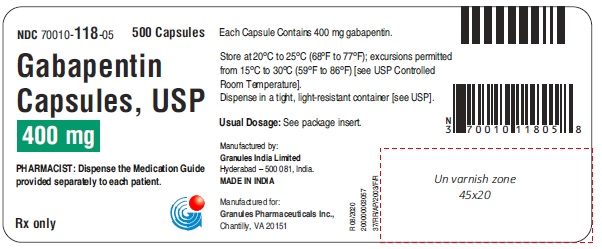
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Capsules Gabapentin capsules, USP 100 mg are available for oral administration as hard gelatin capsules with a white opaque body, white opaque cap, hard gelatine capsule, imprinted G 56 black ink; supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 70010-108-01), bottles of 500 (NDC 70010-108-05), bottles of 1000 (NDC 70010-108-10). Gabapentin capsules, USP 300 mg are available for oral administration as hard gelatin capsules with a white opaque body, yellow opaque cap, hard gelatine capsules, imprinted G 57 black ink; supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 70010-109-01), bottles of 500 (NDC 70010-109-05), bottles of 1000 (NDC 70010-109-10). Gabapentin capsules, USP 400 mg are available for oral administration as hard gelatin capsules with a white opaque body, orange opaque cap, hard gelatine capsules, imprinted G 58 black ink; supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 70010-118-01), bottles of 500 (NDC 70010-118-05), bottles of 1000 (NDC70010-118-10). * Maalox ® is a registered trademark of Novartis Consumer Health Inc. Storage Store gabapentin at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tight, light resistant container [see USP].
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Gabapentin is indicated for: • Management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults • Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy Gabapentin is indicated for: • Postherpetic neuralgia in adults (1) • Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy ( 1 )
Dosage and Administration
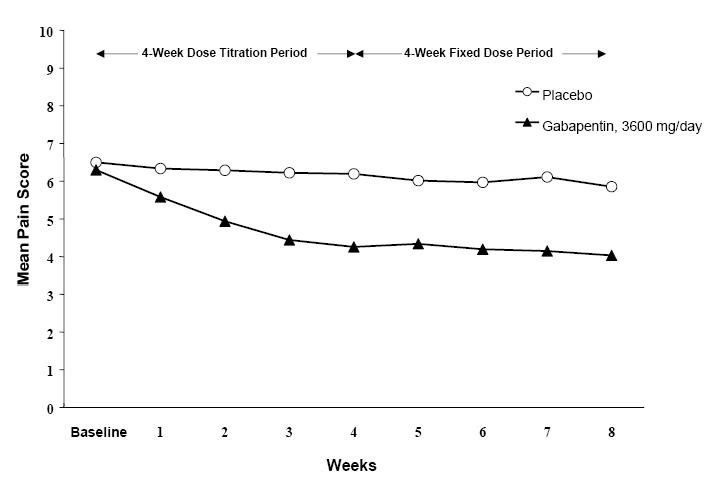
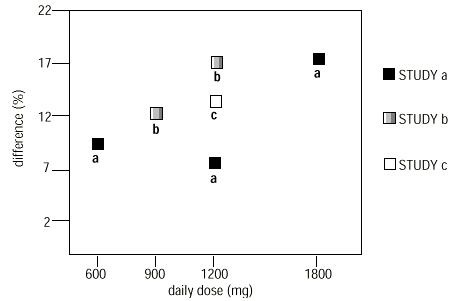
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Postherpetic Neuralgia (2.1) o Dose can be titrated up as needed to a dose of 1800 mg/day o Day 1: Single 300 mg dose o Day 2: 600 mg/day (i.e., 300 mg two times a day) o Day 3: 900 mg/day (i.e., 300 mg three times a day) • Epilepsy with Partial Onset Seizures (2.2) o Patients 12 years of age and older: starting dose is 300 mg three times daily; may be titrated up to 600 mg three times daily o Patients 3 to 11 years of age: starting dose range is 10 to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses; recommended dose in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses; the recommended dose in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended dose is reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days • Dose should be adjusted in patients with reduced renal function ( 2.3 , 2.4 ) 2.1 Dosage for Postherpetic Neuralgia In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). In clinical studies, efficacy was demonstrated over a range of doses from 1800 mg/day to 3600 mg/day with comparable effects across the dose range; however, in these clinical studies, the additional benefit of using doses greater than 1800 mg/day was not demonstrated. 2.2 Dosage for Epilepsy with Partial Onset Seizures Patients 12 years of age and above The starting dose is 300 mg three times a day. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin is 300 mg to 600 mg three times a day. Dosages up to 2400 mg/day have been well tolerated in long-term clinical studies. Doses of 3600 mg/day have also been administered to a small number of patients for a relatively short duration, and have been well tolerated. Administer gabapentin three times a day using 300 mg or 400 mg capsules. The maximum time between doses should not exceed 12 hours. Pediatric Patients Age 3 to 11 years The starting dose range is 10 mg/kg/day to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses, and the recommended maintenance dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. The maximum time interval between doses should not exceed 12 hours. 2.3 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): Ta b le 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function Renal Function Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) Total Daily Dose Range (mg/day) Dose Regimen (mg) ≥ 60 900 to 3600 300 TID 400 TID 600 TID 800 TID 1200 TID >30 to 59 400 to 1400 200 BID 300 BID 400 BID 500 BID 700 BID >15 to 29 200 to 700 200 QD 300 QD 400 QD 500 QD 700 QD 15 a 100 to 300 100 QD 125 QD 150 QD 200 QD 300 QD Post-Hemodialysis Supplemental Dose (mg) b Hemodialysis 125 b 150 b 200 b 250 b 350 b TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose a For patients with creatinine clearance <15 mL/min, reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance (e.g., patients with a creatinine clearance of 7.5 mL/min should receive one-half the daily dose that patients with a creatinine clearance of 15 mL/min receive). b Patients on hemodialysis should receive maintenance doses based on estimates of creatinine clearance as indicated in the upper portion of the table and a supplemental post-hemodialysis dose administered after each 4 hours of hemodialysis as indicated in the lower portion of the table. Creatinine clearance (CLCr) is difficult to measure in outpatients. In patients with stable renal function, creatinine clearance can be reasonably well estimated using the equation of Cockcroft and Gault: The use of gabapentin in patients less than 12 years of age with compromised renal function has not been studied. gabapentin-formula-jpg.jpg 2.4 Dosage in Elderly Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and dose should be adjusted based on creatinine clearance values in these patients. 2.5 Administration Information Administer gabapentin orally with or without food. Gabapentin capsules should be swallowed whole with water. If the gabapentin dose is reduced, discontinued, or substituted with an alternative medication, this should be done gradually over a minimum of 1 week (a longer period may be needed at the discretion of the prescriber).
