Drug Catalog - Product Detail
LIDOCAINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP 2% INJECT. 100MG/5ML 10X5ML
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55150-0165-05 | EUGIA US LLC | 5 | 2% | SOLUTION |
PACKAGE FILES

Generic Name
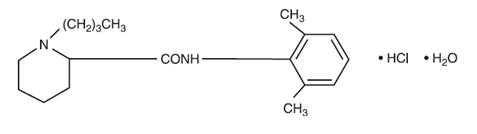
MARCAINE, LIDOCAINE, KENALOG, POVIDONE IODINE
Substance Name
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
EPIDURAL
Application Number
Description
11 DESCRIPTION Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection contains bupivacaine hydrochloride, an amide local anesthetic, as the active pharmaceutical ingredient. The route of administration for Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection is by injection, for infiltration, perineural, caudal, epidural, or retrobulbar use. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] . Bupivacaine hydrochloride is 2-piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl- N -(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-, monohydrochloride, monohydrate. It is a white crystalline powder that is freely soluble in 95 percent ethanol, soluble in water, and slightly soluble in chloroform or acetone. It has the following structural formula: Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is a clear and colorless sterile isotonic solution. Each mL of single-dose vial contains 5 mg of bupivacaine hydrochloride (equivalent to 4.44 mg of bupivacaine, respectively), sodium chloride for isotonicity, sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH between 4 and 6.5, in water for injection. image description
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Store at 20 °C to 25 °C (68 °F to 77 °F); excursions permitted between 15 °C to 30 °C (59 °F to 86 °F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP ─ Solutions of bupivacaine hydrochloride may be autoclaved. Autoclave at 15-pound pressure, 121 °C (250 °F) for 15 minutes. This product is clear and colorless. Do not use the solution if it is discolored or if it contains a precipitate. Unit of Sale Concentration NDC 0409-1162-01 Tray of 25 single-dose teartop vials 0.5% 50 mg/10 mL (5 mg/mL) NDC 0409-1162-02 Tray of 25 single-dose teartop vials 0.5% 150 mg/30 mL (5 mg/mL) For single-dose vials: Discard unused portion.
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection is indicated in adults for the production of local or regional anesthesia or analgesia for surgery, dental and oral surgery procedures, diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, and for obstetrical procedures. Specific concentrations and presentations of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection are recommended for each type of block indicated to produce local or regional anesthesia or analgesia [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ]. Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection contains bupivacaine, an amide local anesthetic. Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection is indicated in adults for the production of local or regional anesthesia or analgesia for surgery, dental and oral surgery procedures, diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, and for obstetrical procedures. For each type of block indicated to produce local or regional anesthesia or analgesia, specific concentrations and presentations are recommended. ( 1 , 2.2 ) Limitations of Use Not all blocks are indicated for use with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection given clinically significant risks associated with use. ( 1 , 2.2 , 4 , 5.1 , 5.5 , 5.7 , 5.9 ) Limitations of Use Not all blocks are indicated for use with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection given clinically significant risks associated with use [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) , Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.5 , 5.7 , 5.9) ] .
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Not for intrathecal use. ( 2.1 ) Avoid use of solutions containing antimicrobial preservatives (i.e., multiple-dose vials) for epidural or caudal anesthesia. ( 2.1 ) See full prescribing information for: - Recommended concentrations and dosages of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection according to type of block. ( 2.2 ) - Additional dosage and administration information pertaining to use in epidural anesthesia and use in ophthalmic surgery. ( 2.3 , 2.6 ) 2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Information Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection is not for intrathecal use. Discard unused portions of solution not containing preservatives, i.e., those supplied in single-dose vials, following initial use. Visually inspect this product for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection are clear, colorless solutions. Do not administer solutions which are discolored or contain particulate matter. Mixing or the prior or intercurrent use of any other local anesthetic with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection is not recommended because of insufficient data on the clinical use of such mixtures. Administration Precautions Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection Injection are to be administered in carefully adjusted dosages by or under the supervision of experienced clinicians who are well versed in the diagnosis and management of dose-related toxicity and other acute emergencies which might arise from the block to be employed. Use Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection only if the following are immediately available: oxygen, cardiopulmonary resuscitative equipment and drugs, and the personnel resources needed for proper management of toxic reactions and related emergencies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Adverse Reactions (6) , Overdosage (10) ] . The toxic effects of local anesthetics are additive. Monitor for neurologic and cardiovascular effects related to local anesthetic systemic toxicity when additional local anesthetics are administered with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Drug Interactions (7.1) , Overdosage (10) ] . Aspirate for blood or cerebrospinal fluid (where applicable) prior to injecting Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, both the initial dose and all subsequent doses, to avoid intravascular or intrathecal injection. However, a negative aspiration for blood or cerebrospinal fluid does not ensure against an intravascular or intrathecal injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ] . Avoid rapid injection of a large volume of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection and use fractional (incremental) doses when feasible. During major regional nerve blocks, such as those of the brachial plexus or lower extremity, the patient should have an indwelling intravenous catheter to assure adequate intravenous access. The lowest dosage of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection that results in effective anesthesia should be used to avoid high plasma levels and serious adverse reactions. Perform careful and constant monitoring of cardiovascular and respiratory (adequacy of oxygenation and ventilation) vital signs and the patient's level of consciousness after each local anesthetic injection. 2.2 Recommended Concentrations and Dosages of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection The dosage of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection administered varies with the anesthetic procedure, the area to be anesthetized, the vascularity of the tissues, the number of neuronal segments to be blocked, the depth of anesthesia and degree of muscle relaxation required, the duration of anesthesia desired, individual tolerance, and the physical condition of the patient. Administer the smallest dosage and concentration required to produce the desired result. The types of block and recommended Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection concentrations are shown in Table 1. Table 1. Types of Block and Recommended Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection Concentrations Type of Block Bupivacaine Hydrochloride injection 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) 0.5% (5 mg/mL) 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL)* Local infiltration ✓ Peripheral nerve block ✓ ✓ Retrobulbar block ✓ Sympathetic block ✓ Caudal block ✓ ✓ Lumbar epidural block ✓ ✓ ✓ (not for obstetrical anesthesia) Epidural test dose Dental block * Bupivacaine Hydrochloride injection 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) is not recommended for nonobstetrical surgical procedures in pregnant patients. ✓= indicated use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. At recommended dosages, Bupivacaine Hydrochloride produces complete sensory block, but the effect on motor function differs among the three concentrations. Table 2 provides information on the expected effect on motor function for the three concentrations. Table 2. Types of Block and Recommended Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection Concentrations Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection Concentration Motor Function 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) When used for caudal, epidural, or peripheral nerve block, produces incomplete motor block. Should be used for operations in which muscle relaxation is not important, or when another means of providing muscle relaxation is used concurrently. Onset of action may be slower than with the 0.5% (5 mg/mL) or 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) solutions. 0.5% (5 mg/mL) Provides motor blockade for caudal, epidural, or nerve block, but muscle relaxation may be inadequate for operations in which complete muscle relaxation is essential. 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) Produces complete motor block. Most useful for epidural block in abdominal operations requiring complete muscle relaxation, and for retrobulbar anesthesia. Not for obstetrical anesthesia. The duration of anesthesia with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection is such that for most indications, a single dose is sufficient. The maximum dosage limit within the recommended dosage range must be individualized in each case after evaluating the size and physical status of the patient, as well as the anticipated rate of systemic absorption from a particular injection site. The dosages in Table 3 are recommended as a guide for use in the average adult. These doses may be repeated once every three hours. Do not exceed a total daily dosage of 400 mg in 24 hours. The duration of anesthetic effect may be prolonged by the addition of epinephrine. Table 3. Recommended Concentrations and Doses of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection in Adults Type of Block Concentration of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection Each Dose Motor Block With continuous (intermittent) techniques, repeat doses increase the degree of motor block. The first repeat dose of 0.5% (5 mg/mL) may produce complete motor block. Intercostal nerve block with 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) also may produce complete motor block for intra-thoracic and upper intra-abdominal surgery. mL mg of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection Local infiltration 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) Solutions with or without epinephrine (i.e., applies to Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection. Up to 70 (without epinephrine) Up to 175 (without epinephrine) ― Up to 90 (with epinephrine) Up to 225 (with epinephrine) Peripheral nerve block 0.5% (5 mg/mL) 5–35 (without epinephrine) 25–175 (without epinephrine) moderate to complete 5–45 (with epinephrine) 25–225 (with epinephrine) 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) 5–70 (without epinephrine) 12.5–175 (without epinephrine) moderate to complete 5–90 (with epinephrine) 12.5–225 (with epinephrine) Retrobulbar block [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) 2–4 15–30 complete Sympathetic block 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) 20–50 50–125 ― Caudal block [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] 0.5% (5 mg/mL) 15–30 75–150 moderate to complete 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) 15–30 37.5–75 moderate Lumbar epidural block [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) For single-dose use; not for intermittent epidural technique. Not for obstetrical anesthesia. 10–20 75–150 complete 0.5% (5 mg/mL) 10–20 50–100 moderate to complete 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) 10–20 25–50 partial to moderate 2.3 Use in Epidural Anesthesia During epidural administration, administer Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, 0.5% (5 mg/mL) and 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) solutions in incremental doses of 3 mL to 5 mL with sufficient time between doses to detect toxic manifestations of unintentional intravascular or intrathecal injection. Administer injections slowly, with frequent aspirations before and during the injection to avoid intravascular injection. Perform syringe aspirations before and during each supplemental injection in continuous (intermittent) catheter techniques. In obstetrics, use ONLY the 0.5% (5 mg/mL) and 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) concentrations of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]; incremental doses of 3 mL to 5 mL of the 0.5% (5 mg/mL) solution not exceeding 50 mg to 100 mg at any dosing interval are recommended. Repeat doses should be preceded by a test dose containing epinephrine if not clinically contraindicated. Use only the single-dose vials for caudal or epidural anesthesia; avoid use of the multiple-dose vials for these procedures, which contain a preservative [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 ) , Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9) ] . 2.6 Use in Ophthalmic Surgery When Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) is used for retrobulbar block, complete corneal anesthesia usually precedes onset of clinically acceptable external ocular muscle akinesia. Therefore, presence of akinesia rather than anesthesia alone should determine readiness of the patient for surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15) ] .
