Drug Catalog - Product Detail
LIOTHYRONINE SODIUMUSP 5MCG TB 100
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62756-0589-88 | SUN PHARMACEUTICALS | 100 | 5MCG | NA |
PACKAGE FILES

Generic Name
LIOTHYRONINE SODIUM
Substance Name
LIOTHYRONINE SODIUM
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA091382
Description
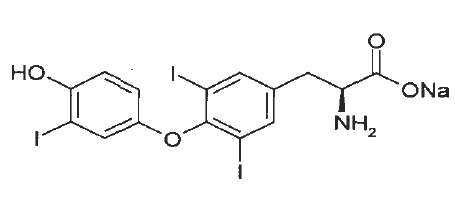
11 DESCRIPTION Liothyronine sodium tablets, USP contain the active ingredient, liothyronine (L-triiodothyronine or LT 3 ), a synthetic form of a thyroid hormone liothyronine in sodium salt form. It is chemically designated as L-Tyrosine, O-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenyl)-3,5-diiodo-, monosodium salt. The molecular formula, molecular weight and structural formula of liothyronine sodium are given below. C 15 H 11 I 3 NNaO 4 M.W.672.96 Liothyronine sodium tablets, USP contain liothyronine sodium, USP equivalent to liothyronine in 5 mcg, 25 mcg, and 50 mcg. Inactive ingredients consist of corn starch, croscarmellose sodium, gelatin type B, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and microcrystalline cellulose. liothyronine-structure
How Supplied
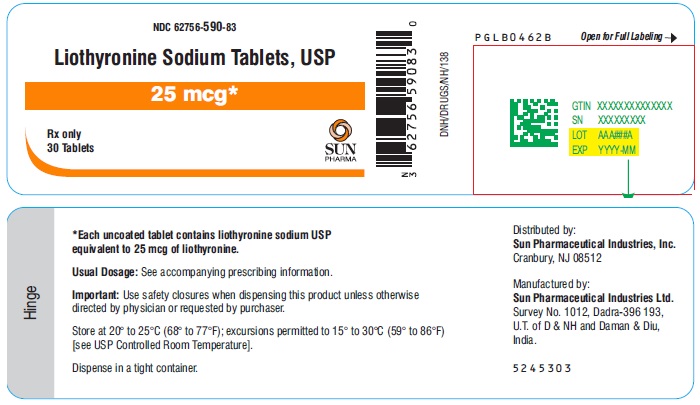
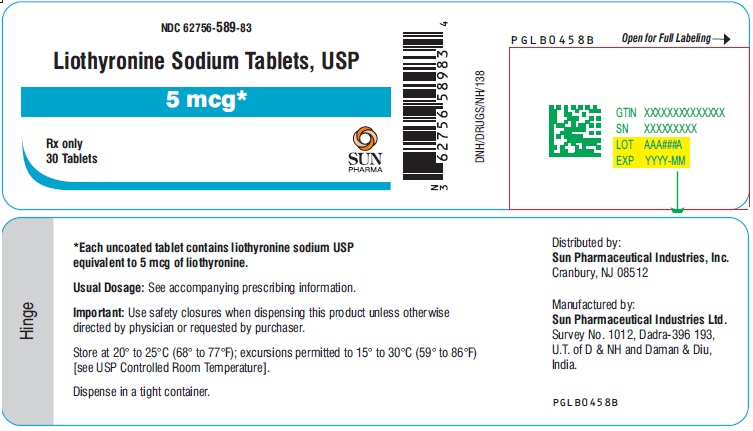
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Liothyronine sodium tablets, USP are white to off-white, circular, uncoated tablets. They are supplied as follows: Liothyronine sodium tablets, containing 5 mcg liothyronine are debossed ‘589’ on one side and plain on other side. Bottles of 30 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-589-83 Bottles of 90 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-589-01 Bottles of 100 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-589-88 Bottles of 100, NDC 62756-589-08 Bottles of 1000, NDC 62756-589-18 Liothyronine sodium tablets, containing 25 mcg liothyronine are debossed ‘590’ on one side and breakline on other side. Bottles of 30 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-590-83 Bottles of 90 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-590-01 Bottles of 100 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-590-88 Bottles of 100, NDC 62756-590-08 Bottles of 1000, NDC 62756-590-18 Liothyronine sodium tablets, containing 50 mcg liothyronine are debossed ‘591’ on one side and breakline on other side. Bottles of 30 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-591-83 Bottles of 90 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-591-01 Bottles of 100 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-591-88 Bottles of 100, NDC 62756-591-08 Bottles of 1000, NDC 62756-591-18 Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Liothyronine is an L-triiodothyronine (T3) indicated for: Hypothyroidism: As replacement in primary (thyroidal), secondary (pituitary), and tertiary (hypothalamic) congenital or acquired hypothyroidism (1.1) Pituitary Thyrotropin (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone, TSH) Suppression: As an adjunct to surgery and radioiodine therapy in the management of well-differentiated thyroid cancer (1.2) Thyroid Suppression Test: As a diagnostic agent in suppression tests to differentiate suspected mild hyperthyroidism or thyroid gland autonomy (1.3) Limitations of Use: Not indicated for suppression of benign thyroid nodules and nontoxic diffuse goiter in iodine-sufficient patients. (1) Not indicated for treatment of hypothyroidism during the recovery phase of subacute thyroiditis. (1) 1.1 Hypothyroidism Liothyronine sodium tablets are indicated as a replacement therapy in primary (thyroidal), secondary (pituitary), and tertiary (hypothalamic) congenital or acquired hypothyroidism. 1.2 Pituitary Thyrotropin (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone, TSH) Suppression Liothyronine sodium tablets are indicated as an adjunct to surgery and radioiodine therapy in the management of well-differentiated thyroid cancer. 1.3 Thyroid Suppression Test Liothyronine sodium tablets are indicated as a diagnostic agent in suppression tests to differentiate suspected mild hyperthyroidism or thyroid gland autonomy. Limitations of Use Liothyronine sodium tablets are not indicated for suppression of benign thyroid nodules and nontoxic diffuse goiter in iodine-sufficient patients as there are no clinical benefits and overtreatment with liothyronine sodium tablets may induce hyperthyroidism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Liothyronine sodium tablets are not indicated for treatment of hypothyroidism during the recovery phase of subacute thyroiditis.
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Administer liothyronine sodium tablets orally once daily and individual dosage according to patient response and laboratory findings (2.1) See full prescribing information for recommended dosage for hypothyroidism (2.2) TSH suppression in well-differentiated thyroid cancer (2.3) and for thyroid suppression test (2.4) When switching a patient to liothyronine sodium tablets discontinue levothyroxine therapy and initiate liothyronine sodium tablets at a low dosage. Gradually increase the dose according to the patient’s response (2.5) Adequacy of therapy determined with periodic monitoring of TSH and T3 levels as well as clinical status (2.6) 2.1 General Principles of Dosing The dose of liothyronine sodium tablets for hypothyroidism or pituitary Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) suppression depends on a variety of factors including: the patient's age, body weight, cardiovascular status, concomitant medical conditions (including pregnancy), concomitant medications, coadministered food and the specific nature of the condition being treated [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3, 2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5), and Drug Interactions (7)] . Dosing must be individualized to account for these factors and dose adjustments made based on periodic assessment of the patient's clinical response and laboratory parameters [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] . Administer liothyronine sodium tablets orally once daily. 2.2 Recommended Dosage for Hypothyroidism Adults The recommended starting dosage is 25 mcg orally once daily. Increase the dose by 25 mcg daily every 1 or 2 weeks, if needed. The usual maintenance dose is 25 mcg to 75 mcg once daily. For elderly patients or patients with underlying cardiac disease, start with liothyronine sodium tablets 5 mcg once daily and increase by 5 mcg increments at the recommended intervals. Serum TSH is not a reliable measure of liothyronine sodium tablets dose adequacy in patients with secondary or tertiary hypothyroidism and should not be used to monitor therapy. Use the serum T3 level to monitor adequacy of therapy in this patient population. Pediatric Patients The recommended starting dosage is 5 mcg once daily, with a 5 mcg increase every 3 to 4 days until the desired response is achieved. Infants a few months old may require 20 mcg once daily for maintenance. At 1 year of age, 50 mcg once daily may be required. Above 3 years of age, the full adult dosage may be necessary [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. Newborns (0 to 3 months) at Risk for Cardiac Failure: Consider a lower starting dose in infants at risk for cardiac failure. Increase the dose as needed based on clinical and laboratory response. Pediatric Patients at Risk for Hyperactivity: To minimize the risk of hyperactivity in pediatric patients, start at one-fourth the recommended full replacement dose, and increase on a weekly basis by one-fourth the full recommended replacement dose until the full recommended replacement dose is reached. Pregnancy Preexisting Hypothyroidism: Thyroid hormone dose requirements may increase during pregnancy. Measure serum TSH and free-T4 as soon as pregnancy is confirmed and, at minimum, during each trimester of pregnancy. In patients with primary hypothyroidism, maintain serum TSH in the trimester-specific reference range. For patients with serum TSH above the normal trimester-specific range, increase the dose of thyroid hormone and measure TSH every 4 weeks until a stable dose is reached and serum TSH is within the normal trimester-specific range. Reduce thyroid hormone dosage to pre-pregnancy levels immediately after delivery and measure serum TSH levels 4 to 8 weeks postpartum to ensure thyroid hormone dose is appropriate. 2.3 Recommended Dosage for TSH Suppression in Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer The dose of liothyronine sodium tablets should target TSH levels within the desired therapeutic range. This may require higher doses, depending on the target level for TSH suppression. 2.4 Recommended Dosage for Thyroid Suppression Test The recommended dose is 75 mcg to 100 mcg daily for 7 days, with radioactive iodine uptake being determined before and after the 7 day administration of liothyronine sodium tablets. If thyroid function is normal, the radioiodine uptake will drop significantly after treatment. A 50% or greater suppression of uptake indicates a normal thyroid-pituitary axis. 2.5 Switching from Levothyroxine to Liothyronine Sodium Tablets Liothyronine sodium has a rapid onset of action and residual effects of the other thyroid preparation may persist for the first several weeks after initiating liothyronine sodium tablets therapy. When switching a patient to liothyronine sodium tablets, discontinue levothyroxine therapy and initiate liothyronine sodium tablets at a low dosage. Gradually increase the liothyronine sodium tablets, dose according to the patient's response. 2.6 Monitoring TSH and Triiodothyronine (T3) Levels Assess the adequacy of therapy by periodic assessment of laboratory tests and clinical evaluation. Persistent clinical and laboratory evidence of hypothyroidism despite an apparent adequate replacement dose of liothyronine sodium tablets may be evidence of inadequate absorption, poor compliance, drug interactions, or a combination of these factors. Adults In adult patients with primary hypothyroidism, monitor serum TSH periodically after initiation of the therapy or any change in dose. To check the immediate response to therapy before the TSH has had a chance to respond or if your patient’s status needs to be assessed prior to that point, measurement of total T3 would be most appropriate. In patients on a stable and appropriate replacement dose, evaluate clinical and biochemical response every 6 to 12 months and whenever there is a change in the patient’s clinical status. Pediatrics In pediatric patients with hypothyroidism, assess the adequacy of replacement therapy by measuring serum TSH and T3 levels. For pediatric patients three years of age and older, the recommended monitoring is every 3 to 12 months thereafter, following dose stabilization until growth and puberty are completed. Poor compliance or abnormal values may necessitate more frequent monitoring. Perform routine clinical examination, including assessment of development, mental and physical growth, and bone maturation, at regular intervals. While the general aim of therapy is to normalize the serum TSH level, TSH may not normalize in some patients due to in utero hypothyroidism causing a resetting of pituitary-thyroid feedback. Failure of the serum TSH to decrease below 20 IU per liter after initiation of liothyronine sodium tablets therapy may indicate the child is not receiving adequate therapy. Assess compliance, dose of medication administered, and method of administration prior to increasing the dose of liothyronine sodium tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] . Secondary and Tertiary Hypothyroidism Monitor serum T3 levels and maintain in the normal range.
