Drug Catalog - Product Detail
POTASSIUM CITRATE TAB ER 15 MEQ (1620 MG) 100 CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 42543-0408-01 | STRIDES PHARMA | 100 | 15 MEQ(1620 MG) | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES
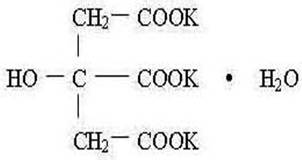



Generic Name
POTASSIUM CITRATE
Substance Name
POTASSIUM CITRATE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA206813
Description
11 DESCRIPTION Potassium citrate USP is a citrate salt of potassium. Its empirical formula is K 3 C 6 H 5 O 7 • H 2 O, and it has the following chemical structure: Potassium citrate extended-release tablets USP are pale yellow colored, oral wax-matrix tablets, contain 5 mEq (540 mg) potassium citrate USP, 10 mEq (1080 mg) potassium citrate USP and 15 mEq (1620 mg) potassium citrate USP each. Inactive ingredients include carnauba wax, stearic acid and magnesium stearate. USP dissolution test is pending. Pot-citrate-Structure
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Potassium citrate extended-release tablets USP 5 mEq are uncoated, pale yellow colored, round shaped, bi-Convex, debossed with 'S406' on one side and plain on the other side, supplied in bottles as: NDC 42543-406-01 Bottle of 100 tablets Potassium citrate extended-release tablets USP 10 mEq are uncoated, pale yellow colored, caplet shaped, bi-Convex, debossed with 'S407' on one side and plain on the other side, supplied in bottles as: NDC 42543-407-01 Bottle of 100 tablets Potassium citrate extended-release tablets USP 15 mEq are uncoated, pale yellow colored, caplet shaped, bi-Convex, debossed with 'S408' on one side and plain on the other side, supplied in bottles as: NDC 42543-408-01 Bottle of 100 tablets Storage : Store in a tight container at 20°–25°C (68°–77°F), Excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F) [See USP controlled room temperature].
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Potassium citrate is a citrate salt of potassium indicated for the management of: • Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) with calcium stones (1.1) • Hypocitraturic calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis of any etiology (1.2) • Uric acid lithiasis with or without calcium stones (1.3) 1.1 Renal Tubular Acidosis (RTA) with Calcium Stones Potassium citrate is indicated for the management of renal tubular acidosis [see Clinical Studies (14.1)] . 1.2 Hypocitraturic Calcium Oxalate Nephrolithiasis of any Etiology Potassium citrate is indicated for the management of Hypocitraturic calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] . 1.3 Uric Acid Llithiasis with or without Calcium Stones Potassium citrate is indicated for the management of Uric acid lithiasis with or without calcium stones [see Clinical Studies (14.3)] .
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Objective: To restore normal urinary citrate (greater than 320 mg/day and as close to the normal mean of 640 mg/day as possible), and to increase urinary pH to a level of 6.0 to 7.0. • Severe hypocitraturia (urinary citrate < 150 mg/day): therapy should be initiated at 60 mEq per day; a dose of 30 mEq two times per day or 20 mEq three times per day with meals or within 30 minutes after meals or bedtime snack (2.2) • Mild to moderate hypocitraturia (urinary citrate >150 mg/day): therapy should be initiated at 30 mEq per day; a dose of 15 mEq two times per day or 10 mEq three times per day with meals or within 30 minutes after meals or bedtime snack (2.3) 2.1 Dosing Instructions Treatment with extended release potassium citrate should be added to a regimen that limits salt intake (avoidance of foods with high salt content and of added salt at the table) and encourages high fluid intake (urine volume should be at least two litres per day). The objective of treatment with potassium citrate extended-release tablets is to provide potassium citrate in sufficient dosage to restore normal urinary citrate (greater than 320 mg/day and as close to the normal mean of 640 mg/day as possible), and to increase urinary pH to a level of 6.0 or 7.0. Monitor serum electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chloride and carbon dioxide), serum creatinine and complete blood counts every four months and more frequently in patients with cardiac disease, renal disease or acidosis. Perform electrocardiograms periodically. Treatment should be discontinued if there is hyperkalemia, a significant rise in serum creatinine or a significant fall in blood hematocrit or hemoglobin. 2.2 Severe Hypocitraturia In patients with severe hypocitraturia (urinary citrate < 150 mg/day), therapy should be initiated at a dosage of 60 mEq /day (30 mEq two times/day or 20 mEq three times/day with meals or within 30 minutes after meals or bedtime snack). Twenty-four hour urinary citrate and/or urinary pH measurements should be used to determine the adequacy of the initial dosage and to evaluate the effectiveness of any dosage change. In addition, urinary citrate and/or pH should be measured every four months. Doses of potassium citrate extended-release tablets greater than 100 mEq/day have not been studied and should be avoided. 2.3 Mild to Moderate Hypocitraturia In patients with mild to moderate hypocitraturia (urinary citrate > 150 mg/day) therapy should be initiated at 30 mEq/day (15 mEq two times/day or 10 mEq three times/day with meals or within 30 minutes after meals or bedtime snack). Twenty-four hour urinary citrate and/or urinary pH measurements should be used to determine the adequacy of the initial dosage and to evaluate the effectiveness of any dosage change. Doses of Potassium citrate extended-release tablets greater than 100 mEq/day have not been studied and should be avoided.
