Drug Catalog - Product Detail
SPIRONOLACTONE 50MG TB 100
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68382-0661-01 | ZYDUS PHARMACEUTICALS (USA) | 100 | 50MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES
Generic Name
SPIRONOLACTONE
Substance Name
SPIRONOLACTONE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA205936
Description
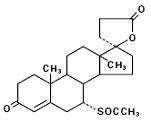
11 DESCRIPTION Spironolactone tablets, USP contain 25 mg, 50 mg, or 100 mg of the aldosterone antagonist spironolactone, 17-hydroxy-7α-mercapto-3-oxo-17α-pregn-4-ene-21-carboxylic acid γ-lactone acetate, which has the following structural formula: Spironolactone, USP is practically insoluble in water, soluble in ethyl acetate and alcohol, freely soluble in benzene and in chloroform, slightly soluble in menthanol and very slightly soluble in fixed oils. Inactive ingredients include calcium sulfate dihydrate, colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, peppermint flavor, povidone and sodium lauryl sulfate. Additionally each tablet contains opadry II white 33F28398 which contains hydroxylpropyl methyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol, talc and titanium dioxide. Image
How Supplied
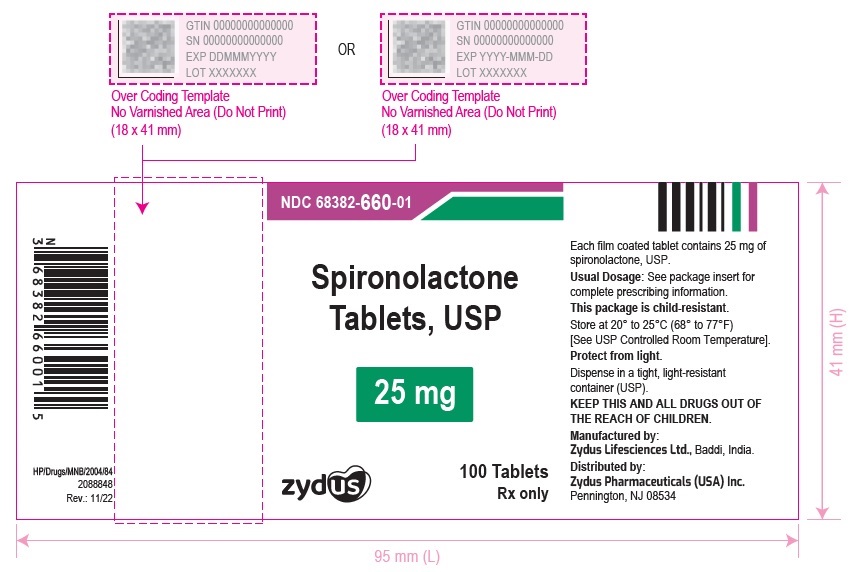
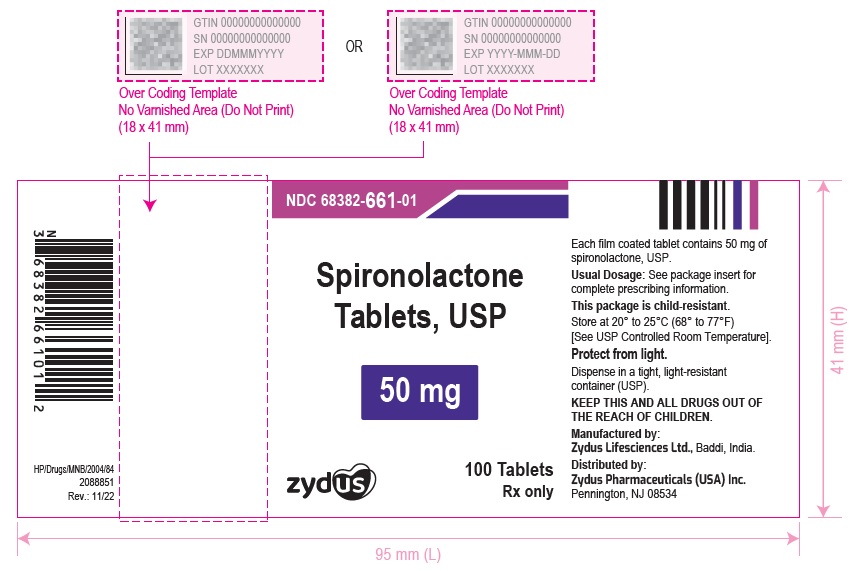
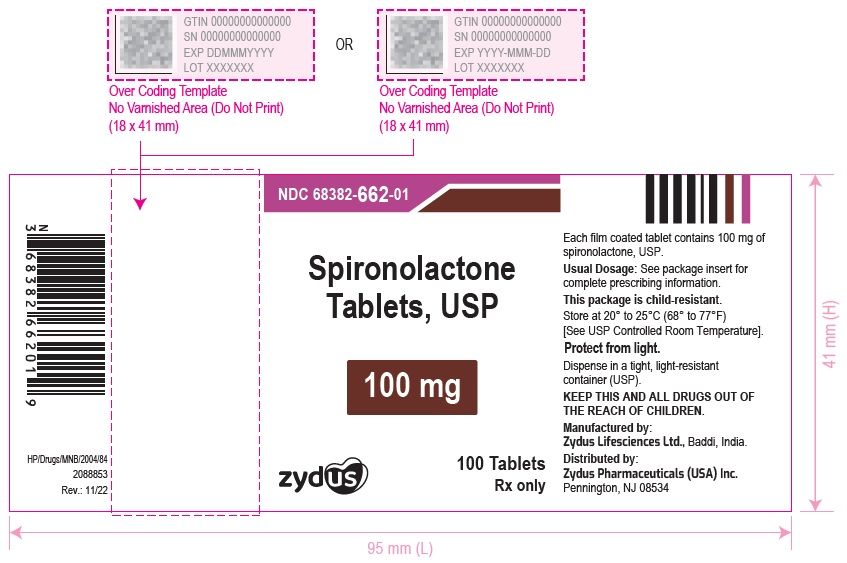
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Spironolactone Tablets USP, 25 mg are white to off-white, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with '660' on one side and plain on the other side and are supplied as follows: NDC 68382-660-06 in bottles of 30 tablets with child-resistant closure NDC 68382-660-16 in bottles of 90 tablets with child-resistant closure NDC 68382-660-01 in bottles of 100 tablets with child-resistant closure NDC 68382-660-05 in bottles of 500 tablets NDC 68382-660-10 in bottles of 1000 tablets NDC 68382-660-30 in unit-dose blister cartons of 100 (10 x 10) unit-dose tablets Spironolactone Tablets USP, 50 mg are white to off-white, oval shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with '661' on the scored side and plain on the other side and are supplied as follows: NDC 68382-661-06 in bottles of 30 tablets with child-resistant closure NDC 68382-661-16 in bottles of 90 tablets with child-resistant closure NDC 68382-661-01 in bottles of 100 tablets with child-resistant closure NDC 68382-661-05 in bottles of 500 tablets NDC 68382-661-10 in bottles of 1000 tablets NDC 68382-661-30 in unit-dose blister cartons of 100 (10 x 10) unit-dose tablets Spironolactone Tablets USP, 100 mg are white to off-white, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with '662' on one side and scored on the other side and are supplied as follows: NDC 68382-662-06 in bottles of 30 tablets with child-resistant closure NDC 68382-662-16 in bottles of 90 tablets with child-resistant closure NDC 68382-662-01 in bottles of 100 tablets with child-resistant closure NDC 68382-662-05 in bottles of 500 tablets NDC 68382-662-10 in bottles of 1000 tablets NDC 68382-662-30 in unit-dose blister cartons of 100 (10 x 10) unit-dose tablets Storage Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature] . Protect from light. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container (USP).
Indications & Usage
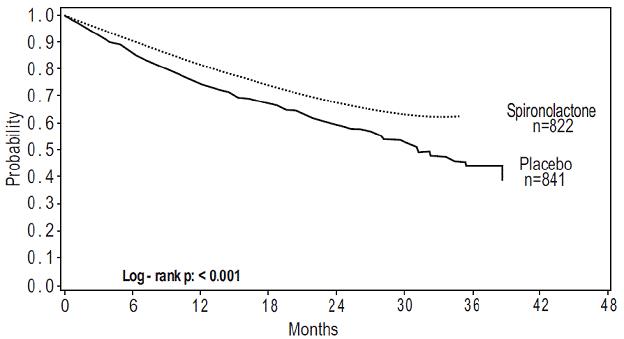
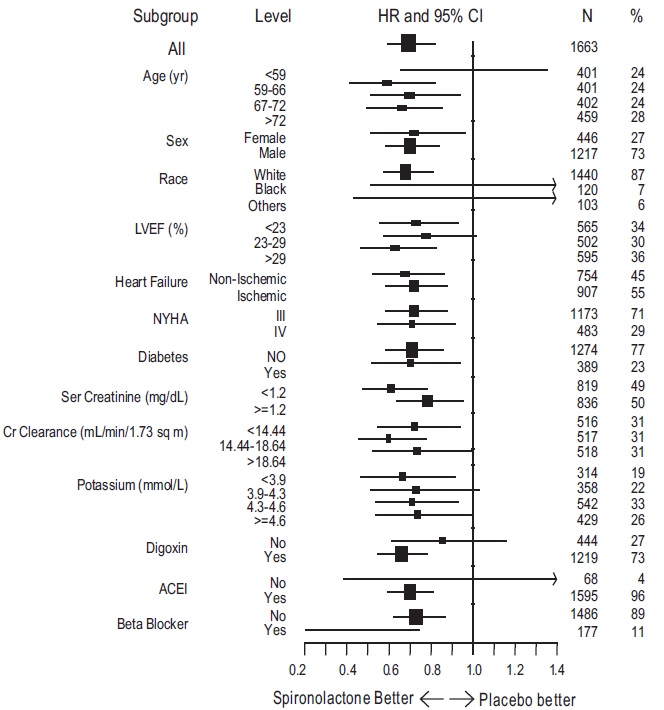
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Spironolactone is an aldosterone antagonist indicated for: The treatment of NYHA Class III-IV heart failure and reduced ejection fraction to increase survival, manage edema, and to reduce the need for hospitalization for heart failure ( 1.1 ). Use as an add-on therapy for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions ( 1.2 ). The management of edema in adult patients who are cirrhotic when edema is not responsive to fluid and sodium restrictions and in the setting of nephrotic syndrome when treatment of the underlying disease, restriction of fluid and sodium intake, and the use of other diuretics produce an inadequate response ( 1.3 ). Treatment of primary hyperaldosternism for: ( 1.4 ) Short-term preoperative treatment Long-term maintenance for patients with discrete aldosterone-producing adrenal adenomas who are not candidates for surgery and patients with bilateral micro or macronodular adrenal hyperplasia 1.1 Heart Failure Spironolactone tablets are indicated for treatment of NYHA Class III-IV heart failure and reduced ejection fraction to increase survival, manage edema, and reduce the need for hospitalization for heart failure. Spironolactone tablets are usually administered in conjunction with other heart failure therapies. 1.2 Hypertension Spironolactone tablets are indicated as add-on therapy for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure in patients who are not adequately controlled on other agents. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes. Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than one drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program's Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC). Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly. Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal. Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy. 1.3 Edema Associated with Hepatic Cirrhosis or Nephrotic Syndrome Spironolactone tablets are indicated for the management of edema in the following settings: Cirrhosis of the liver when edema is not responsive to fluid and sodium restriction. Nephrotic syndrome when treatment of the underlying disease, restriction of fluid and sodium intake, and the use of other diuretics produce an inadequate response. Because it increases serum potassium, spironolactone may be useful for treating edema when administration of other diuretics has caused hypokalemia. 1.4 Primary Hyperaldosteronism Spironolactone tablets are indicated in the following settings: Short-term preoperative treatment of patients with primary hyperaldosteronism. Long-term maintenance therapy for patients with discrete aldosterone-producing adrenal adenomas who are not candidates for surgery. Long-term maintenance therapy for patients with bilateral micro or macronodular adrenal hyperplasia (idiopathic hyperaldosteronism).
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Heart Failure: Initiate treatment at 25 mg once daily ( 2.2 ). Hypertension: Initiate treatment at 25 mg to 100 mg daily in either single or divided doses ( 2.3 ). Edema: Initiate therapy in a hospital setting and titrate slowly. The recommended initial daily dose is 100 mg in single or divided doses ( 2.4 ). Primary hyperaldosteronism: Initiate treatment at 100 mg to 400 mg in preparation for surgery. In patients unsuitable for surgery use the lowest effective dosage determined for the individual patient ( 2.5 ). 2.1 General Considerations Spironolactone can be taken with or without food, but should be taken consistently with respect to food [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )] . 2.2 Treatment of Heart Failure In patients with serum potassium ≤5.0 mEq/L and eGFR >50 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , initiate treatment at 25 mg once daily. Patients who tolerate 25 mg once daily may have their dosage increased to 50 mg once daily as clinically indicated. Patients who develop hyperkalemia on 25 mg once daily may have their dosage reduced to 25 mg every other day [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )] . In patients with an eGFR between 30 and 50 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , consider initiating therapy at 25 mg every other day because of the risk of hyperkalemia [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.6 )]. 2.3 Treatment of Essential Hypertension The recommended initial daily dose is 25 mg to 100 mg of spironolactone administered in either single or divided doses is recommended. Dosage can be titrated at two-week intervals. Doses greater than 100 mg/day generally do not provide additional reductions in blood pressure. 2.4 Treatment of Edema In patients with cirrhosis, initiate therapy in a hospital setting and titrate slowly [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.7 )] . The recommended initial daily dosage is 100 mg of spironolactone administered in either single or divided doses, but may range from 25 mg to 200 mg daily. When given as the sole agent for diuresis, administer for at least five days before increasing dose to obtain desired effect. 2.5 Treatment of Primary Hyperaldosteronism Administer spironolactone in doses of 100 mg to 400 mg daily in preparation for surgery. For patients who are considered unsuitable for surgery, spironolactone can be used as long-term maintenance therapy at the lowest effective dosage determined for the individual patient.
