Drug Catalog - Product Detail
SULINDAC 200MG TB 500CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 53489-0479-05 | SUN PHARMACEUTICALS | 500 | 200MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES


Generic Name
SULINDAC
Substance Name
SULINDAC
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA072050
Description
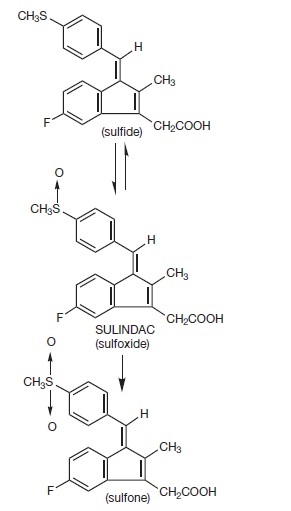
DESCRIPTION Sulindac is a non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory indene derivative designated chemically as (Z)-5-fluoro-2-methyl-1-[[ p -(methylsulfinyl)phenyl]methylene]-1 H -indene-3-acetic acid. It is not a salicylate, pyrazolone or propionic acid derivative. Its empirical formula is C 20 H 17 FO 3 S, with a molecular weight of 356.42. Sulindac, a yellow crystalline compound, is a weak organic acid practically insoluble in water below pH 4.5, but very soluble as the sodium salt or in buffers of pH 6 or higher. Sulindac tablets are available in 150 and 200 mg tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and pregelatinized starch. Following absorption, sulindac undergoes two major biotransformations — reversible reduction to the sulfide metabolite, and irreversible oxidation to the sulfone metabolite. Available evidence indicates that the biological activity resides with the sulfide metabolite. The structural formulas of sulindac and its metabolites are: structure
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Sulindac tablets USP are supplied as follows: Sulindac tablets, 150 mg, yellow, round, unscored, debossed MP 112 Bottles of 50 NDC 53489-478-02 Bottles of 60 NDC 53489-478-06 Bottles of 100 NDC 53489-478-01 Bottles of 250 NDC 53489-478-03 Bottles of 500 NDC 53489-478-05 Bottles of 1000 NDC 53489-478-10 Sulindac tablets, 200 mg, yellow, round, scored, debossed MP 116 Bottles of 50 NDC 53489-479-02 Bottles of 60 NDC 53489-479-06 Bottles of 100 NDC 53489-479-01 Bottles of 250 NDC 53489-479-03 Bottles of 500 NDC 53489-479-05 Bottles of 1000 NDC 53489-479-10 Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature] DISPENSE IN TIGHT, LIGHT-RESISTANT CONTAINER.
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of sulindac tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use sulindac tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS ). Sulindac tablets are indicated for acute or long-term use in the relief of signs and symptoms of the following: Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid arthritis* Ankylosing spondylitis Acute painful shoulder (Acute subacromial bursitis/supraspinatus tendinitis) Acute gouty arthritis
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of sulindac tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use sulindac tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS ). After observing the response to initial therapy with sulindac tablets, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient's needs. Sulindac tablets should be administered orally twice a day with food. The maximum dosage is 400 mg per day. Dosages above 400 mg per day are not recommended. In osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis, the recommended starting dosage is 150 mg twice a day. The dosage may be lowered or raised depending on the response. A prompt response (within one week) can be expected in about one-half of patients with osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Others may require longer to respond. In acute painful shoulder (acute subacromial bursitis/supraspinatus tendinitis) and acute gouty arthritis, the recommended dosage is 200 mg twice a day. After a satisfactory response has been achieved, the dosage may be reduced according to the response. In acute painful shoulder, therapy for 7–14 days is usually adequate. In acute gouty arthritis, therapy for 7 days is usually adequate. **Incidence between 3% and 9%. Those reactions occurring in 1% to 3% of patients are not marked with an asterisk.
