Drug Catalog - Product Detail
VERAPAMIL HCL ER CAPS. CP 100MG 100
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62175-0485-37 | KREMERS URBAN | 100 | 100MG | CAPSULE |
PACKAGE FILES


Generic Name
VERAPAMIL HYDROCHLORIDE
Substance Name
VERAPAMIL HYDROCHLORIDE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
NDA020943
Description
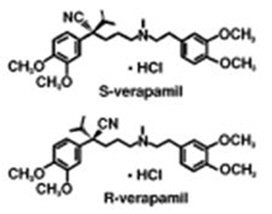
11 DESCRIPTION Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) is a calcium ion influx inhibitor (slow channel blocker or calcium ion antagonist). Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) is available for oral administration as a 100 mg hard gelatin capsule (white opaque cap/amethyst body), a 200 mg hard gelatin capsule (amethyst opaque cap/amethyst body), and as a 300 mg hard gelatin capsule (lavender opaque cap/amethyst body). Verapamil is administered as a racemic mixture of the R and S enantiomers. The structural formulae of the verapamil HCl enantiomers are: C 27 H 38 N 2 O 4 ∙HCl M.W.=491.07 Chemical name: Benzeneacetonitrile, α-[3-[[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]methylamino]propyl]- 3,4-dimethoxy-α-(1-methylethyl)-, monohydrochloride,(±)-. Verapamil HCl is an almost white, crystalline powder, practically free of odor, with a bitter taste. It is soluble in water, chloroform and methanol. Verapamil HCl is not structurally related to other cardioactive drugs. In addition to verapamil HCl the Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: D&C Red #28, FD & C Blue #1, FD&C red #40, fumaric acid, gelatin, povidone, shellac, silicon dioxide, sodium lauryl sulfate, starch, sugar spheres, talc, and titanium dioxide. System Components and Performance: Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) uses the proprietary CODAS ® (Chronotherapeutic Oral Drug Absorption System) technology, which is designed for bedtime dosing, incorporating a 4 to 5-hour delay in drug delivery. The controlled-onset delivery system results in a maximum plasma concentration (C max ) of verapamil in the morning hours. These pellet filled capsules provide for extended-release of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract. The Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) formulation has been designed to initiate the release of verapamil 4-5 hours after ingestion. This delay is introduced by the level of non-enteric release-controlling polymer applied to drug loaded beads. The release-controlling polymer is a combination of water soluble and water insoluble polymers. As water from the gastrointestinal tract comes into contact with the polymer coated beads, the water soluble polymer slowly dissolves and the drug diffuses through the resulting pores in the coating. The water insoluble polymer continues to act as a barrier, maintaining the controlled release of the drug. The rate of release is essentially independent of pH, posture and food. Multiparticulate systems such as Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) have been shown to be independent of gastrointestinal motility. Chemical Structure
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) (verapamil hydrochloride) extended-release pellet filled capsules are supplied in three dosage strengths: 100 mg: Two piece size 2 hard gelatin capsule, white opaque cap and amethyst body imprinted KU/485 100 mg. Product identification printed in black ink, supplied as follows: NDC 62175-485-37 Bottle of 100s 200 mg: Two piece size 0 hard gelatin capsule, amethyst opaque cap and amethyst body imprinted KU/486 200 mg. Product identification printed in black ink, supplied as follows: NDC 62175-486-37 Bottle of 100s 300 mg: Two piece size 00 hard gelatin capsule, lavender opaque cap and amethyst body imprinted KU/487 300 mg. Product identification printed in black ink, supplied as follows: NDC 62175-487-37 Bottle of 100s Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture. Dispense in tight, light-resistant container as defined in USP.
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) for oral use is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes including this drug. Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than one drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program's Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC). Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly. Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal. Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy. Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) is a calcium channel blocker indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. ( 1 )
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION THE CONTENTS OF THE Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) CAPSULE SHOULD NOT BE CRUSHED OR CHEWED. Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) CAPSULES ARE TO BE SWALLOWED WHOLE OR THE ENTIRE CONTENTS OF THE CAPSULE SPRINKLED ONTO APPLESAUCE. Do not crush or chew capsule contents; swallow capsule whole or sprinkle entire contents onto applesauce ( 2.2 , 17 ) Usual dosage: 200 mg once daily at bedtime; if inadequate response, titrate upward to 300 mg, then 400 mg once daily at bedtime ( 2.1 ) Initial dose of 100 mg once daily at bedtime in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, elderly or low-weight patients ( 2.1 ) 2.1 Essential Hypertension Administer Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) once daily at bedtime. Clinical trials studied doses of 100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg. The usual daily dose of extended-release Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) in clinical trials has been 200 mg given by mouth once daily at bedtime. In rare instances, initial doses of 100 mg a day may be warranted in patients who have an increased response to verapamil [e.g. patients with impaired renal function, impaired hepatic function, elderly, low-weight patients, etc. ( see Use in Specific Populations (8.5 , 8.6 , 8.7) )]. Base upward titration on therapeutic efficacy and safety evaluated approximately 24 hours after dosing. The antihypertensive effects of Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) are evident within the first week of therapy. If an adequate response is not obtained with 200 mg of Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM), the dose may be titrated upward in the following manner: a) 300 mg each evening b) 400 mg each evening (2 × 200 mg) When Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) is administered at bedtime, office evaluation of blood pressure during morning and early afternoon hours is essentially a measure of peak effect. The usual evaluation of trough effect, which sometimes might be needed to evaluate the appropriateness of any given dose of Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM), would be just prior to bedtime. 2.2 Sprinkling the Capsule Contents on Food Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) capsules may also be administered by carefully opening the capsule and sprinkling the pellets onto one tablespoonful of applesauce. Swallow the applesauce immediately without chewing and follow with a glass of cool water to ensure complete swallowing of the pellets. The applesauce used should not be hot and it should be soft enough to be swallowed without chewing. Use any pellet/applesauce mixture immediately and do not store for future use. Absorption of the pellets sprinkled onto other foods has not been tested. This method of administration may be beneficial for patients who have difficulty swallowing whole capsules. Subdividing the contents of a Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (PM) capsule is not recommended.
